Chronic Intermittent Ethanol Exposure Dysregulates Nucleus Basalis Magnocellularis Afferents in the Basolateral Amygdala
- PMID: 36280288
- PMCID: PMC9668348
- DOI: 10.1523/ENEURO.0164-22.2022
Chronic Intermittent Ethanol Exposure Dysregulates Nucleus Basalis Magnocellularis Afferents in the Basolateral Amygdala
Abstract
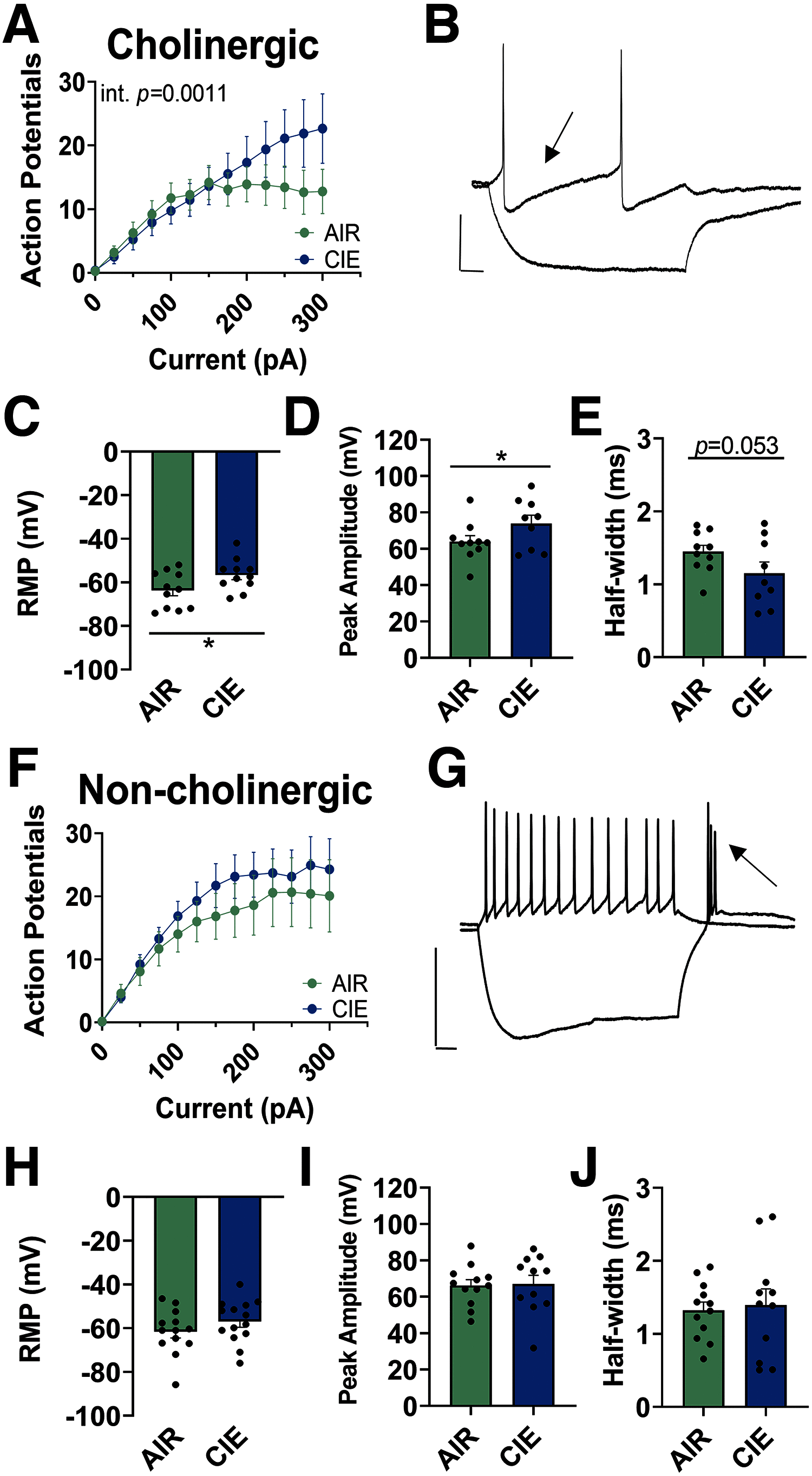
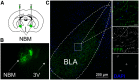
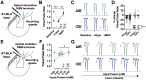
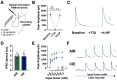
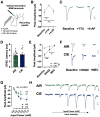
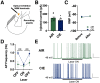
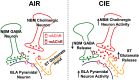
Nucleus basalis magnocellularis (NBM) cholinergic projections to the basolateral amygdala (BLA) regulate the acquisition and consolidation of fear-like and anxiety-like behaviors. However, it is unclear whether the alterations in the NBM-BLA circuit promote negative affect during ethanol withdrawal (WD). Therefore, we performed ex vivo whole-cell patch-clamp electrophysiology in both the NBM and the BLA of male Sprague Dawley rats following 10 d of chronic intermittent ethanol (CIE) exposure and 24 h of WD. We found that CIE exposure and withdrawal enhanced the neuronal excitability of NBM putative "cholinergic" neurons. We subsequently used optogenetics to directly manipulate NBM terminal activity within the BLA and measure cholinergic modulation of glutamatergic afferents and BLA pyramidal neurons. Our findings indicate that CIE and withdrawal upregulate NBM cholinergic facilitation of glutamate release via activation of presynaptic nicotinic acetylcholine receptors (AChRs). Ethanol withdrawal-induced increases in NBM terminal activity also enhance BLA pyramidal neuron firing. Collectively, our results provide a novel characterization of the NBM-BLA circuit and suggest that CIE-dependent modifications to NBM afferents enhance BLA pyramidal neuron activity during ethanol withdrawal.
Keywords: GABA; acetylcholine; amygdala; basal forebrain; ethanol; glutamate.
Copyright © 2022 Sizer et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures
References
-
- Aitta-Aho T, Hay YA, Phillips BU, Saksida LM, Bussey TJ, Paulsen O, Apergis-Schoute J (2018) Basal forebrain and brainstem cholinergic neurons differentially impact amygdala circuits and learning-related behavior. Curr Biol 28:2557–2569.e4. - PubMed
-
- Alonso A, Khateb A, Fort P, Jones BE, Mühlethaler M (1996) Differential oscillatory properties of cholinergic and noncholinergic nucleus basalis neurons in guinea pig brain slice. Eur J Neurosci 8:169–182. - PubMed
-
- Arieli E, Gerbi R, Shein-Idelson M, Moran A (2020) Temporally-precise basolateral amygdala activation is required for the formation of taste memories in gustatory cortex. J Physiol 598:5505–5522. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
