Convergent actions of stress and stimulants via epigenetic regulation of neural circuitry
- PMID: 36280459
- PMCID: PMC9671852
- DOI: 10.1016/j.tins.2022.10.001
Convergent actions of stress and stimulants via epigenetic regulation of neural circuitry
Abstract
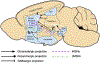
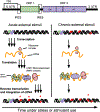
The dorsal striatum integrates prior and current information to guide appropriate decision-making. Chronic stress and stimulant exposure interferes with decision-making, and can confer similar cognitive and behavioral inflexibilities. This review examines the literature on acute and chronic regulation of the epigenome by stress and stimulants. Recent evidence suggests that exposures to stress and stimulants share similarities in the manners in which they regulate the dorsal striatum epigenome through DNA methylation, transposable element activity, and histone post-translational modifications. These findings suggest that chronic stress and stimulant exposure leads to the accumulation of epigenetic modifications that impair immediate and future neuron function and activity. Such epigenetic mechanisms represent potential therapeutic targets for ameliorating convergent symptoms of stress and addiction.
Keywords: addiction; chronic stress; decision-making; dorsal striatum; transposable elements.
Copyright © 2022 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier Ltd.. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests The authors declare no competing interests in relation to this work.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Epigenetic landscape of amphetamine and methamphetamine addiction in rodents.Epigenetics. 2015;10(7):574-80. doi: 10.1080/15592294.2015.1055441. Epigenetics. 2015. PMID: 26023847 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Epigenetic Regulatory Dynamics in Models of Methamphetamine-Use Disorder.Genes (Basel). 2021 Oct 14;12(10):1614. doi: 10.3390/genes12101614. Genes (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34681009 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Epigenetic Mechanisms of Psychostimulant-Induced Addiction.Int Rev Neurobiol. 2015;120:85-105. doi: 10.1016/bs.irn.2015.02.010. Epub 2015 Apr 8. Int Rev Neurobiol. 2015. PMID: 26070754 Review.
-
Epigenomics in stress tolerance of plants under the climate change.Mol Biol Rep. 2023 Jul;50(7):6201-6216. doi: 10.1007/s11033-023-08539-6. Epub 2023 Jun 9. Mol Biol Rep. 2023. PMID: 37294468 Review.
-
Epigenetic interplay of histone modifications and DNA methylation mediated by HDA6.Plant Signal Behav. 2012 Jun;7(6):633-5. doi: 10.4161/psb.19994. Epub 2012 May 14. Plant Signal Behav. 2012. PMID: 22580702 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Neurobiological intersections of stress and substance use disorders.Front Neurosci. 2025 May 1;19:1548372. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2025.1548372. eCollection 2025. Front Neurosci. 2025. PMID: 40376607 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The evolving neurobiology of early-life stress.Neuron. 2025 May 21;113(10):1474-1490. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2025.02.016. Epub 2025 Mar 17. Neuron. 2025. PMID: 40101719 Review.
-
UTX deletion promotes M2 macrophage polarization by epigenetically regulating endothelial cell-macrophage crosstalk after spinal cord injury.J Nanobiotechnology. 2023 Jul 15;21(1):225. doi: 10.1186/s12951-023-01986-0. J Nanobiotechnology. 2023. PMID: 37454119 Free PMC article.
-
Assessing the Expression of Long INterspersed Elements (LINEs) via Long-Read Sequencing in Diverse Human Tissues and Cell Lines.Genes (Basel). 2023 Sep 29;14(10):1893. doi: 10.3390/genes14101893. Genes (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37895242 Free PMC article.
-
Early life adversity: Epigenetic regulation underlying drug addiction susceptibility.Mol Cell Neurosci. 2023 Jun;125:103825. doi: 10.1016/j.mcn.2023.103825. Epub 2023 Feb 24. Mol Cell Neurosci. 2023. PMID: 36842544 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

