ROCK1/MLC2 inhibition induces decay of viral mRNA in BPXV infected cells
- PMID: 36280692
- PMCID: PMC9592580
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-022-21610-9
ROCK1/MLC2 inhibition induces decay of viral mRNA in BPXV infected cells
Abstract
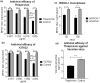
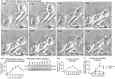
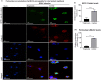
Rho-associated coiled-coil containing protein kinase 1 (ROCK1) intracellular cell signaling pathway regulates cell morphology, polarity, and cytoskeletal remodeling. We observed the activation of ROCK1/myosin light chain (MLC2) signaling pathway in buffalopox virus (BPXV) infected Vero cells. ROCK1 depletion by siRNA and specific small molecule chemical inhibitors (Thiazovivin and Y27632) resulted in a reduced BPXV replication, as evidenced by reductions in viral mRNA/protein synthesis, genome copy numbers and progeny virus particles. Further, we demonstrated that ROCK1 inhibition promotes deadenylation of viral mRNA (mRNA decay), mediated via inhibiting interaction with PABP [(poly(A)-binding protein] and enhancing the expression of CCR4-NOT (a multi-protein complex that plays an important role in deadenylation of mRNA). In addition, ROCK1/MLC2 mediated cell contraction, and perinuclear accumulation of p-MLC2 was shown to positively correlate with viral mRNA/protein synthesis. Finally, it was demonstrated that the long-term sequential passage (P = 50) of BPXV in the presence of Thiazovivin does not select for any drug-resistant virus variants. In conclusion, ROCK1/MLC2 cell signaling pathway facilitates BPXV replication by preventing viral mRNA decay and that the inhibitors targeting this pathway may have novel therapeutic effects against buffalopox.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
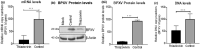

References
-
- Moss, B. Poxviridae: the viruses and their replication, vol. 2. Knipe, DMl (2001).
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

