Automated synapse-level reconstruction of neural circuits in the larval zebrafish brain
- PMID: 36280717
- PMCID: PMC9636024
- DOI: 10.1038/s41592-022-01621-0
Automated synapse-level reconstruction of neural circuits in the larval zebrafish brain
Abstract
Dense reconstruction of synaptic connectivity requires high-resolution electron microscopy images of entire brains and tools to efficiently trace neuronal wires across the volume. To generate such a resource, we sectioned and imaged a larval zebrafish brain by serial block-face electron microscopy at a voxel size of 14 × 14 × 25 nm3. We segmented the resulting dataset with the flood-filling network algorithm, automated the detection of chemical synapses and validated the results by comparisons to transmission electron microscopic images and light-microscopic reconstructions. Neurons and their connections are stored in the form of a queryable and expandable digital address book. We reconstructed a network of 208 neurons involved in visual motion processing, most of them located in the pretectum, which had been functionally characterized in the same specimen by two-photon calcium imaging. Moreover, we mapped all 407 presynaptic and postsynaptic partners of two superficial interneurons in the tectum. The resource developed here serves as a foundation for synaptic-resolution circuit analyses in the zebrafish nervous system.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
F.S., J.K. and A.A.W. are founders and owners of ariadne.ai ag (Switzerland). M.J. is an employee of Google LLC, which sells cloud computing services. The remaining authors declare no competing interests.
Figures








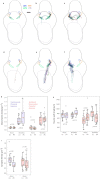
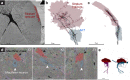
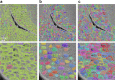

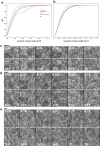


Comment in
-
Mapping of the zebrafish brain takes shape.Nat Methods. 2022 Nov;19(11):1345-1346. doi: 10.1038/s41592-022-01637-6. Nat Methods. 2022. PMID: 36280716 No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
Methods for Mapping Neuronal Activity to Synaptic Connectivity: Lessons From Larval Zebrafish.Front Neural Circuits. 2018 Oct 25;12:89. doi: 10.3389/fncir.2018.00089. eCollection 2018. Front Neural Circuits. 2018. PMID: 30410437 Free PMC article.
-
Whole-brain serial-section electron microscopy in larval zebrafish.Nature. 2017 May 18;545(7654):345-349. doi: 10.1038/nature22356. Epub 2017 May 10. Nature. 2017. PMID: 28489821 Free PMC article.
-
High-resolution whole-brain staining for electron microscopic circuit reconstruction.Nat Methods. 2015 Jun;12(6):541-6. doi: 10.1038/nmeth.3361. Epub 2015 Apr 13. Nat Methods. 2015. PMID: 25867849
-
Challenges of microtome-based serial block-face scanning electron microscopy in neuroscience.J Microsc. 2015 Aug;259(2):137-142. doi: 10.1111/jmi.12244. Epub 2015 Apr 23. J Microsc. 2015. PMID: 25907464 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Beyond counts and shapes: studying pathology of dendritic spines in the context of the surrounding neuropil through serial section electron microscopy.Neuroscience. 2013 Oct 22;251:75-89. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2012.04.061. Epub 2012 May 1. Neuroscience. 2013. PMID: 22561733 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Neural interfaces: Bridging the brain to the world beyond healthcare.Exploration (Beijing). 2024 Mar 14;4(5):20230146. doi: 10.1002/EXP.20230146. eCollection 2024 Oct. Exploration (Beijing). 2024. PMID: 39439491 Free PMC article.
-
Zebrafish as a Model for Multiple Sclerosis.Biomedicines. 2024 Oct 16;12(10):2354. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines12102354. Biomedicines. 2024. PMID: 39457666 Free PMC article. Review.
-
An ultrastructural map of a spinal sensorimotor circuit reveals the potential of astroglial modulation.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2025 Mar 6:2025.03.05.641432. doi: 10.1101/2025.03.05.641432. bioRxiv. 2025. PMID: 40093104 Free PMC article. Preprint.
-
The myeloid cell-driven transdifferentiation of endothelial cells into pericytes promotes the restoration of BBB function and brain self-repair after stroke.Elife. 2025 Jul 16;14:RP105593. doi: 10.7554/eLife.105593. Elife. 2025. PMID: 40667795 Free PMC article.
-
SyConn2: dense synaptic connectivity inference for volume electron microscopy.Nat Methods. 2022 Nov;19(11):1367-1370. doi: 10.1038/s41592-022-01624-x. Epub 2022 Oct 24. Nat Methods. 2022. PMID: 36280715 Free PMC article.
References
-
- White JG, Southgate E, Thomson JN, Brenner S. The structure of the nervous system of the nematode Caenorhabditis elegans. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. B Biol. Sci. 1986;314:1–340. - PubMed
-
- Bargmann CI, Marder E. From the connectome to brain function. Nat. Methods. 2013;10:483–490. - PubMed
-
- Ohyama T, et al. A multilevel multimodal circuit enhances action selection in Drosophila. Nature. 2015;520:633–639. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

