A combined polygenic score of 21,293 rare and 22 common variants improves diabetes diagnosis based on hemoglobin A1C levels
- PMID: 36280733
- PMCID: PMC9995082
- DOI: 10.1038/s41588-022-01200-1
A combined polygenic score of 21,293 rare and 22 common variants improves diabetes diagnosis based on hemoglobin A1C levels
Abstract
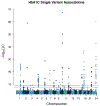
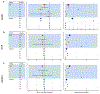
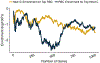
Polygenic scores (PGSs) combine the effects of common genetic variants1,2 to predict risk or treatment strategies for complex diseases3-7. Adding rare variation to PGSs has largely unknown benefits and is methodically challenging. Here, we developed a method for constructing rare variant PGSs and applied it to calculate genetically modified hemoglobin A1C thresholds for type 2 diabetes (T2D) diagnosis7-10. The resultant rare variant PGS is highly polygenic (21,293 variants across 154 genes), depends on ultra-rare variants (72.7% observed in fewer than three people) and identifies significantly more undiagnosed T2D cases than expected by chance (odds ratio = 2.71; P = 1.51 × 10-6). A PGS combining common and rare variants is expected to identify 4.9 million misdiagnosed T2D cases in the United States-nearly 1.5-fold more than the common variant PGS alone. These results provide a method for constructing complex trait PGSs from rare variants and suggest that rare variants will augment common variants in precision medicine approaches for common disease.
© 2022. The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Springer Nature America, Inc.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Impact of common genetic determinants of Hemoglobin A1c on type 2 diabetes risk and diagnosis in ancestrally diverse populations: A transethnic genome-wide meta-analysis.PLoS Med. 2017 Sep 12;14(9):e1002383. doi: 10.1371/journal.pmed.1002383. eCollection 2017 Sep. PLoS Med. 2017. PMID: 28898252 Free PMC article.
-
Polygenic subtype identified in ACCORD trial displays a favorable type 2 diabetes phenotype in the UKBiobank population.Hum Genomics. 2024 Jun 22;18(1):70. doi: 10.1186/s40246-024-00639-z. Hum Genomics. 2024. PMID: 38909264 Free PMC article.
-
Addressing the challenges of polygenic scores in human genetic research.Am J Hum Genet. 2022 Dec 1;109(12):2095-2100. doi: 10.1016/j.ajhg.2022.10.012. Am J Hum Genet. 2022. PMID: 36459976 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Complex trait associations in rare diseases and impacts on Mendelian variant interpretation.Nat Commun. 2024 Sep 18;15(1):8196. doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-52407-1. Nat Commun. 2024. PMID: 39294130 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of Genetic Determinants of HbA1c on Type 2 Diabetes Risk and Diagnosis.Curr Diab Rep. 2018 Jun 21;18(8):52. doi: 10.1007/s11892-018-1022-4. Curr Diab Rep. 2018. PMID: 29931457 Review.
Cited by
-
Polygenic score development in the era of large-scale biobanks.Cell Genom. 2022 Jan 13;2(1):100088. doi: 10.1016/j.xgen.2021.100088. eCollection 2022 Jan 12. Cell Genom. 2022. PMID: 36777037 Free PMC article.
-
Bridging the diversity gap: Analytical and study design considerations for improving the accuracy of trans-ancestry genetic prediction.HGG Adv. 2023 Jun 15;4(3):100214. doi: 10.1016/j.xhgg.2023.100214. eCollection 2023 Jul 13. HGG Adv. 2023. PMID: 37448981 Free PMC article.
-
Integration of polygenic and gut metagenomic risk prediction for common diseases.Nat Aging. 2024 Apr;4(4):584-594. doi: 10.1038/s43587-024-00590-7. Epub 2024 Mar 25. Nat Aging. 2024. PMID: 38528230 Free PMC article.
-
Rare loss of function variants in the hepatokine gene INHBE protect from abdominal obesity.Nat Commun. 2022 Jul 27;13(1):4319. doi: 10.1038/s41467-022-31757-8. Nat Commun. 2022. PMID: 35896531 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical use of polygenic scores in type 2 diabetes: challenges and possibilities.Diabetologia. 2025 Jul;68(7):1361-1374. doi: 10.1007/s00125-025-06419-1. Epub 2025 Apr 5. Diabetologia. 2025. PMID: 40186687 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Methods-only references
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01 DK078616/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK125490/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UM1 DK105554/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- K23 DK114551/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- K99 DK127196/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL105756/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK063491/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- K24 HL157960/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR001881/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK105554/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R03 DK131249/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL151855/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- UM1 DK078616/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States

