CD8+ T cells induce interferon-responsive oligodendrocytes and microglia in white matter aging
- PMID: 36280798
- PMCID: PMC9630119
- DOI: 10.1038/s41593-022-01183-6
CD8+ T cells induce interferon-responsive oligodendrocytes and microglia in white matter aging
Abstract
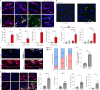
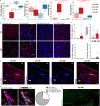
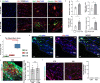
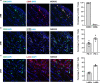
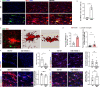
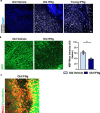
A hallmark of nervous system aging is a decline of white matter volume and function, but the underlying mechanisms leading to white matter pathology are unknown. In the present study, we found age-related alterations of oligodendrocyte cell state with a reduction in total oligodendrocyte density in aging murine white matter. Using single-cell RNA-sequencing, we identified interferon (IFN)-responsive oligodendrocytes, which localize in proximity to CD8+ T cells in aging white matter. Absence of functional lymphocytes decreased the number of IFN-responsive oligodendrocytes and rescued oligodendrocyte loss, whereas T-cell checkpoint inhibition worsened the aging response. In addition, we identified a subpopulation of lymphocyte-dependent, IFN-responsive microglia in the vicinity of the CD8+ T cells in aging white matter. In summary, we provide evidence that CD8+ T-cell-induced, IFN-responsive oligodendrocytes and microglia are important modifiers of white matter aging.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures








Comment in
-
T cells drive aging of the brain.Nat Immunol. 2023 Jan;24(1):12-13. doi: 10.1038/s41590-022-01390-0. Nat Immunol. 2023. PMID: 36596892 No abstract available.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

