Implementation of evidence on management of pleural diseases: insights from a territory-wide survey of clinicians in Hong Kong
- PMID: 36280817
- PMCID: PMC9590185
- DOI: 10.1186/s12890-022-02196-4
Implementation of evidence on management of pleural diseases: insights from a territory-wide survey of clinicians in Hong Kong
Abstract
Background: Major advances in management of common pleural diseases have taken place in the past decade. However, pleural diseases are often managed by physicians of diverse training background and research on implementation of new knowledge is scanty. We aim to evaluate the practice pattern in pleural medicine among physicians in Hong Kong, for identification of possible gaps for clinical service improvement.
Methods: The Hong Kong Thoracic Society undertook a cross-sectional questionnaire survey in 2019, targeting clinicians of various subspecialties in internal medicine and levels of experience (basic and higher trainees, specialists) from twelve regional hospitals of diverse service scopes throughout Hong Kong. Respondents were selected by non-probability quota sampling. The questionnaire tool consisted of 46 questions covering diagnostic and therapeutic aspects of common pleural diseases. The responses were anonymous, and analysed independently using SPSS statistics software.
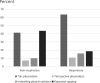
Results: The survey collected 129 responses, 47(36%) were from clinicians specialized in respiratory medicine. Majority of the respondents (98%) managed pleural diseases, including performing pleural procedures in their practice. Fifty-five percent of all the respondents had not received any formal training in transthoracic ultrasonography. A significant proportion of clinicians were unaware of pleuroscopy for investigation of exudative pleural effusion, indwelling pleural catheter for recurrent malignant pleural effusion, and combined intra-pleural Alteplase plus DNase for treatment of pleural infection (30%, 15% and 70% of non-respiratory clinicians respectively). Significant heterogeneity was found in the management of pleural infection, malignant pleural effusion and pneumothorax among respiratory versus non-respiratory clinicians. Contributing factors to the observed heterogeneity included lack of awareness or training, limited accessibility of drugs, devices, or dedicated service support.
Conclusion: Significant heterogeneity in management of pleural diseases was observed among medical clinicians in Hong Kong. Continuous medical education and training provision for both specialists and non-specialists has to be strengthened to enhance the implementation of advances, improve quality and equity of healthcare provision in pleural medicine.
Keywords: Exudative pleural effusion; Malignant pleural effusion; Pleural diseases; Pleural infection; Pneumothorax; Survey; Training; Ultrasonography.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests
Figures
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous