Methotrexate improves endothelial function in early rheumatoid arthritis patients after 3 months of treatment
- PMID: 36280849
- PMCID: PMC9590167
- DOI: 10.1186/s13075-022-02930-7
Methotrexate improves endothelial function in early rheumatoid arthritis patients after 3 months of treatment
Abstract
Background: Endothelial dysfunction contributes to increased cardiovascular (CV) disease in rheumatoid arthritis (RA). Angiogenic T cells (Tang) are a key regulator of vascular function via their interaction with endothelial progenitor cells (EPCs). Methotrexate (MTX) has been associated to reduced CV disease risk, but its effects on endothelial homeostasis have been poorly explored. We investigated MTX effects on endothelial homeostasis in early, treatment-naïve RA patients.
Methods: Fifteen untreated, early RA patients and matched healthy controls (HC) were enrolled. RA patients with long-standing disease in remission or low disease activity treated with MTX for at least 6 months were selected as controls. Circulating CD28+ and CD28null Tang cell, endothelial microparticle (EMP), EPC and soluble vascular cell adhesion molecule (sVCAM)-1 levels were measured.
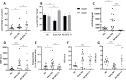
Results: Tang percentage was higher in early RA than in HCs and significantly increased after 3-month MTX treatment. Tang cells in RA were characterized by higher percentage of CD28null and lower CD28-positive cells than HCs. MTX restored a Tang cell phenotype similar to HCs. Altered sVCAM-1, EMP and EPC were restored to levels similar to HCs after a 3-month MTX. Biomarker levels after 3 months of MTX were not different to those of patients with long-standing treatment.
Conclusions: MTX has a positive effect on Tang, sVCAM-1, EPCs and EMPs in RA. Restoration of imbalance between CD28 + and CD28null Tang by MTX may be one of the mechanisms underlying its favourable effects on endothelial dysfunction. These effects seem to be long-lasting and independent from systemic inflammation reduction, suggesting a direct effect of MTX on the endothelium.
Keywords: Angiogenic T cells; Cardiovascular disease; Endothelial dysfunction; Methotrexate; Microvesicles; Platelets; Rheumatoid arthritis.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
An immunological biomarker to predict MTX response in early RA.Ann Rheum Dis. 2014 Nov;73(11):2047-53. doi: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2013-203566. Epub 2013 Aug 29. Ann Rheum Dis. 2014. PMID: 23989988
-
The IMMENSE Study: The Interplay Between iMMune and ENdothelial Cells in Mediating Cardiovascular Risk in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus.Front Immunol. 2020 Oct 29;11:572876. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.572876. eCollection 2020. Front Immunol. 2020. PMID: 33193356 Free PMC article.
-
Soluble cell adhesion molecules (sICAM-1, sVCAM-1, and sE-selectin) in patients with early rheumatoid arthritis.Scand J Rheumatol. 2007 Sep-Oct;36(5):345-50. doi: 10.1080/03009740701406460. Scand J Rheumatol. 2007. PMID: 17963163
-
Methotrexate: a gold standard for treatment of rheumatoid arthritis.J Pain Palliat Care Pharmacother. 2014 Dec;28(4):351-8. doi: 10.3109/15360288.2014.959238. Epub 2014 Oct 16. J Pain Palliat Care Pharmacother. 2014. PMID: 25322199 Review.
-
Predicting methotrexate resistance in rheumatoid arthritis patients.Inflammopharmacology. 2018 Jun;26(3):699-708. doi: 10.1007/s10787-018-0459-z. Epub 2018 Mar 12. Inflammopharmacology. 2018. PMID: 29532212 Review.
Cited by
-
The Inflammatory Link of Rheumatoid Arthritis and Thrombosis: Pathogenic Molecular Circuits and Treatment Approaches.Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2025 Apr 18;47(4):291. doi: 10.3390/cimb47040291. Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2025. PMID: 40699690 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Falcinelli E, Francisci D, Belfiori B, Petito E, Guglielmini G, Malincarne L, et al. In vivo platelet activation and platelet hyperreactivity in abacavir-treated HIV-infected patients. Thromb Haemost. 2013;110:349–357. - PubMed
-
- Falcinelli E, Cosmi B, Filippini M, Petito E, Legnani C, Cini M, et al. Endothelial activation in patients with superficial vein thrombosis (SVT) of the lower limbs. Thromb Res. 2017;157:20–22. - PubMed
-
- Francisci D, Falcinelli E, Belfiori B, Petito E, Fierro T, Baldelli F, et al. Impact of tenofovir versus abacavir on HIV-related endothelial dysfunction. AIDS Patient Care STDs. 2011;25:567–569. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

