Collaborative medication management for older adults after hospital discharge: a qualitative descriptive study
- PMID: 36280875
- PMCID: PMC9590396
- DOI: 10.1186/s12912-022-01061-3
Collaborative medication management for older adults after hospital discharge: a qualitative descriptive study
Abstract
Background: Safe medication management for older adults after hospital discharge requires a well-coordinated, interprofessional, patient-centered approach. This study aimed to describe the perceived needs for collaborative medication management for older adults taking several different medications at home after hospital discharge.
Methods: A qualitative descriptive study was conducted using semi-structured interviews with older adults (n = 28), informal (n = 17), and professional caregivers (n = 13).
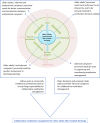
Results: Findings revealed four main needs: older adults and informal caregivers' perceived needs for greater involvement in discharge planning; older adults' perceived needs to be informed, listened to, and to be actively involved in decision-making; informal caregivers' perceived needs for help in supporting and coordinating medication management; and older adults' and informal and professional caregivers' perceived needs for better communication and coordination between professional caregivers.
Conclusion: This study revealed two underutilized pathways towards improving collaborative medication management: medication follow-up involving a community healthcare professional taking an overarching responsibility and empowering older adults and their informal caregivers in medication management after hospital discharge.
Keywords: Collaborative medication management; Discharge planning; Home-dwelling; Informal caregivers; Older adults; Polypharmacy; Qualitative descriptive research; Switzerland.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declared no potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and publication of this article.
Figures
Comment in
-
Involving community healthcare professionals and empowering older adults and their informal carers may improve medication management following hospital discharge.Evid Based Nurs. 2023 Jul;26(3):113. doi: 10.1136/ebnurs-2022-103664. Epub 2023 Feb 6. Evid Based Nurs. 2023. PMID: 36746620 No abstract available.
References
-
- World Health Organization. Medication without harm. Geneva; 2017.
-
- Tariq RA, Vashisht R, Sinha A, Scherbak Y. Medication dispensing errors and prevention. 2018. - PubMed
-
- Monégat M, Sermet C, Perronnin M, Rococo E. Polypharmacy: definitions, measurement and stakes involved. Review of the literature and measurement tests. 2014.
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources