Quantification of multidrug-resistant M. tuberculosis bacilli in sputum during the first 8 weeks of treatment
- PMID: 36281051
- PMCID: PMC9720669
- DOI: 10.5588/ijtld.21.0741
Quantification of multidrug-resistant M. tuberculosis bacilli in sputum during the first 8 weeks of treatment
Abstract
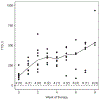
SETTING: Mulago Hospital, Kampala, Uganda.OBJECTIVE: To quantify Mycobacterium tuberculosis in sputum during the first 8 weeks of pulmonary multidrug-resistant TB (MDR-TB) treatment.DESIGN: We enrolled consecutive adults with pulmonary MDR-TB treated according to national guidelines. We collected overnight sputum samples before treatment and weekly. Sputum samples were cultured on Middlebrook 7H11S agar to measure colony-forming units per mL (cfu/mL) and in MGIT™ 960™ media to measure time to detection (TTD). Linear mixed-effects regression was used to estimate the relational change in log10 cfu/mL and TTD.RESULTS: Twelve adults (median age: 27 years) were enrolled. Half were women, and two-thirds were HIV-positive. At baseline, median log10 cfu/mL was 5.1, decreasing by 0.29 log10 cfu/mL/week. The median TTD was 116.5 h, increasing in TTD by 36.97 h/week. The weekly change was greater in the first 2 weeks (-1.04 log10 cfu/mL/week and 120.02 h/week) than in the remaining 6 weeks (-0.17 log10 cfu/mL/week and 26.11 h/week).CONCLUSION: Serial quantitative culture measures indicate a slow, uneven rate of decline in sputum M. tuberculosis over 8 weeks of standardized pulmonary MDR-TB treatment.
CONTEXTE:: Hôpital de Mulago, Kampala, Ouganda.
OBJECTIF:: Quantifier Mycobacterium tuberculosis dans les échantillons de crachats pendant les huit premières semaines du traitement de la TB pulmonaire multirésistante (MDR-TB).
MÉTHODE:: Nous avons inclus, de manière consécutive, des adultes atteints de MDR-TB pulmonaire traités conformément aux recommandations nationales. Nous avons recueilli les échantillons de crachats nocturnes avant l’instauration du traitement, ainsi qu’une fois par semaine. Les échantillons de crachats ont été mis en culture sur gélose Middlebrook 7H11S afin de mesurer les unités formant colonies par mL (cfu/mL) et en milieu MGIT™ 960™ pour mesurer le temps avant détection (TTD). Une régression linéaire à effets mixtes a été utilisée afin d’estimer le changement relatif en log10 cfu/mL et TTD.
RÉSULTATS:: Douze adultes (âge médian : 27 ans) ont été inclus. La moitié était des femmes et les deux tiers étaient infectés par le VIH. Lors de l’inclusion, la valeur log10 cfu/mL médiane était de 5,1, diminuant à 0,29 log10 cfu/mL/semaine. Le TTD médian était de 116,5 h, avec une augmentation du TTD de 36,97 h/semaine. Le changement hebdomadaire était plus important au cours des deux premières semaines (−1,04 log10 cfu/mL/semaine et 120,02 heures/semaine) qu’au cours des six semaines restantes (−0,17 log10 cfu/mL/semaine et 26,11 heures/semaine).
CONCLUSION:: Les mesures quantitatives en série des cultures indiquent un taux de décroissance faible et irrégulier de M. tuberculosis dans les échantillons de crachats au cours de 8 semaines d’un traitement standardisé de la MDR-TB pulmonaire.
Figures



References
-
- Fox W, Ellard GA, Mitchison DA. Studies on the treatment of tuberculosis undertaken by the British Medical Research Council Tuberculosis Units, 1946–1986, with relevant subsequent publications. Int J Tuberc Lung Dis 1999;3:S231–S279. - PubMed
-
- Jindani A, et al. The early bactericidal activity of drugs in patients with pulmonary tuberculosis. Am Rev Respir Dis 1980;121:939–949. - PubMed
-
- Donald PR, Diacon AH. The early bactericidal activity of antituberculosis drugs: a literature review. Tuberculosis 2008;88:S75–83. - PubMed
-
- Domínguez-Castellano A, et al. Factors associated with time to sputum smear conversion in active pulmonary tuberculosis. Int J Tuberc Lung Dis 2003;7:432–438. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

