Expression profile and prognostic values of SMC family members in HCC
- PMID: 36281130
- PMCID: PMC9592487
- DOI: 10.1097/MD.0000000000031336
Expression profile and prognostic values of SMC family members in HCC
Abstract
Objective: The structural maintenance of chromosome (SMC) gene family, including 6 proteins, is involved in a wide range of biological functions in different human cancers. Nevertheless, there is little research on the expression patterns, potential functions and prognostic value of SMC genes in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). Based on publicly available databases and integrative bioinformatics analysis, we tried to determine the value of SMC gene expression in predicting the risk of developing HCC.
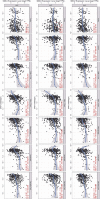
Methods: The expression and copy number variations data of SMC family members were obtained from TCGA (The Cancer Genome Atlas). We identified the prognostic values of SMC family members and their clinical features. GSEA (Gene Set Enrichment Analysis) was conducted to detect the mechanism underlying the involvement of SMC family members in liver cancer. We used Tumor Immune Estimation Resource database to explore the associations between TIICs (Tumor Immune Infiltrating Cells) and the SMC family members.
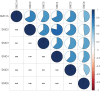
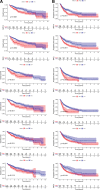
Results: Our analysis proved that downregulation of SMC family members was common modification in HCC patients. In HCC, the expression of SMC1A, SMC2, SMC3, SMC4, SMC6 were upregulated. Upregulation of SMC2, SMC3, and SMC4, along with the clinical stage of HCC, were associated with a poor prognosis according to the results of univariate and multivariate Cox proportional hazards regression analysis. SMC2, SMC3, and SMC4 are also related to tumor purity and immune infiltration levels of HCC. The GSEA results proved that SMC family members take part in numerous biological processes underlying tumorigenesis.
Conclusion: In this study, we comprehensively analyzed the expression of SMC family members in patients with HCC. This can provide insights for further investigation of the SMC members as potential therapeutic targets in HCC and suggest that the use of SMC inhibitor targeting SMC2, SMC3, and SMC4 can be a practical strategy for the therapy of HCC.
Copyright © 2022 the Author(s). Published by Wolters Kluwer Health, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no funding and conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures



References
-
- Llovet JM, Zucman-Rossi J, Pikarsky E, et al. . Hepatocellular carcinoma. Nat Rev Dis Primers. 2021;7:6. - PubMed
-
- Villanueva A. Hepatocellular carcinoma. N Engl J Med. 2019;380:1450–62. - PubMed
-
- Bray F, Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, et al. . Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 2018;68:394–424. - PubMed
-
- Sia D, Villanueva A, Friedman SL, et al. . Liver cancer cell of origin, molecular class, and effects on patient prognosis. Gastroenterology. 2017;152:745–61. - PubMed
-
- Nishiwaki T, Daigo Y, Kawasoe T, et al. . Isolation and characterization of a human cDNA homologous to the Xenopus laevis XCAP-C gene belonging to the structural maintenance of chromosomes (SMC) family. J Hum Genet. 1999;44:197–202. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

