Inhaled Nitric Oxide in Acute Severe Pulmonary Hypertension and Severe Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome Secondary to COVID-19 Pneumonia: A Case Report
- PMID: 36281210
- PMCID: PMC9619383
- DOI: 10.12659/AJCR.937147
Inhaled Nitric Oxide in Acute Severe Pulmonary Hypertension and Severe Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome Secondary to COVID-19 Pneumonia: A Case Report
Abstract
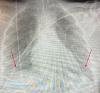
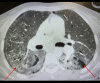
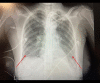
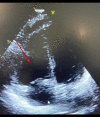
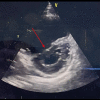
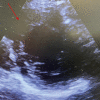
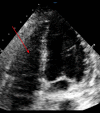
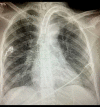
BACKGROUND Inhaled nitric oxide (iNO) is used as a treatment for pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH). Severe hypoxia with hypoxic vasoconstriction caused by severe acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) can induce pulmonary hypertension with hemodynamic implications, mainly secondary to right ventricle (RV) systolic function impairment. We report the case of the use of iNO in a critically ill patient with bilateral SARS-CoV-2 pneumonia and severe ARDS and hypoxemia leading to acute severe PAH, causing a ventilation/perfusion mismatch, RV pressure overload, and RV systolic dysfunction. CASE REPORT A 36-year-old woman was admitted to the Intensive Care Unit with a severe ARDS associated with SARS-CoV-2 pneumonia requiring invasive mechanical ventilation. Severe hypoxia and hypoxic vasoconstriction developed, leading to an acute increase in pulmonary vascular resistance, severe to moderate tricuspid regurgitation, RV pressure overload, RV systolic function impairment, and RV dilatation. Following 24 h of treatment with iNO at 15 ppm, significant oxygenation and hemodynamic improvement were noted, allowing vasopressors to be stopped. After 24 h of iNO treatment, echocardiography showed very mild tricuspid regurgitation, a non-dilated RV, no impairment of transverse free wall contractility, and no paradoxical septal motion. iNO was maintained for 7 days. The dose of iNO was progressively decreased with no adverse effects and maintaining an improvement of oxygenation and hemodynamic status, allowing respiratory weaning. CONCLUSIONS Sustained acute hypoxia in ARDS secondary to SARS-CoV-2 pneumonia can lead to PAH, causing a ventilation/perfusion mismatch and RV systolic impairment. iNO can be considered in patients with significant PAH causing hypoxemia and RV dysfunction.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

References
-
- Griffiths MJ, Evans TW. Inhaled nitric oxide therapy in adults. N Engl J Med. 2005;353:2683–95. - PubMed
-
- Nathan SD, Flaherty KR, Glassberg MK, et al. A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study to assess the safety and efficacy of pulsed, inhaled nitric oxide at a dose of 30 mg/Kg ideal body weight/hr in subjects at risk of pulmonary hypertension associated with pulmonary fibrosis receiving oxygen therapy. Chest. 2020;158(2):637–45. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

