Improvement in sagittal alignment and mechanical low-back pain following deep brain stimulation for Parkinson's disease: illustrative case
- PMID: 36281475
- PMCID: PMC9592960
- DOI: 10.3171/CASE22357
Improvement in sagittal alignment and mechanical low-back pain following deep brain stimulation for Parkinson's disease: illustrative case
Abstract
Background: Parkinson's disease (PD) is a common neurogenerative disease marked by the characteristic triad of bradykinesia, rigidity, and tremor. A significant percentage of patients with PD also demonstrate postural abnormalities (camptocormia) that limit ambulation and accelerate degenerative pathologies of the spine. Although deep brain stimulation (DBS) is a well-established treatment for the motor fluctuations and tremor seen in PD, the efficacy of DBS on postural abnormalities in these patients is less clear.
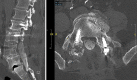
Observations: The authors present a patient with a history of PD and prior lumbosacral fusion who underwent bilateral subthalamic nucleus DBS and experienced immediate improvement in sagittal alignment and subjective relief of mechanical low-back pain.
Lessons: DBS may improve postural abnormalities seen in PD and potentially delay or reduce the need for spinal deformity surgery.
Keywords: Parkinson’s disease; camptocormia; deep brain stimulation; sagittal alignment.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

References
-
- Tysnes OB, Storstein A. Epidemiology of Parkinson’s disease. J Neural Transm (Vienna) 2017;124(8):901–905. - PubMed
-
- Doherty KM, van de Warrenburg BP, Peralta MC, et al. Postural deformities in Parkinson’s disease. Lancet Neurol. 2011;10(6):538–549. - PubMed
-
- Chieng LO, Madhavan K, Wang MY. Deep brain stimulation as a treatment for Parkinson’s disease related camptocormia. J Clin Neurosci. 2015;22(10):1555–1561. - PubMed
-
- Chan AK, Chan AY, Lau D, et al. Surgical management of camptocormia in Parkinson’s disease: systematic review and meta-analysis. J Neurosurg. 2018;131(2):368–375. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

