PTSD, major depression, and advanced transcriptomic age in brain tissue
- PMID: 36281744
- PMCID: PMC9729392
- DOI: 10.1002/da.23289
PTSD, major depression, and advanced transcriptomic age in brain tissue
Abstract
Background: Psychiatric disorders have been associated with advanced epigenetic age in DNA methylation, yet this relationship has not been studied in the brain transcriptome. We examined transcriptomic age using an RNA-based algorithm recently developed by Ren and Kuan ("RNAAgeCalc") and the associations between posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD), major depressive disorder (MDD), and alcohol use disorder with age-adjusted RNA age ("RNA age residuals") in three brain regions: dorsolateral prefrontal cortex, ventromedial prefrontal cortex (vmPFC), and motor cortex.
Methods: RNA sequencing was used to measure gene expression in postmortem brain tissue from the VA National PTSD Brain Bank (n = 94; 59% male).
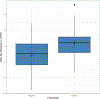
Results: Linear models revealed that diagnoses of PTSD and/or MDD were positively associated with RNA age residuals in vmPFC only (p-adj = 0.012). Three genes in the RNAAgeCalc algorithm (KCNJ16, HYAL2, and CEBPB) were also differentially expressed in association with PTSD/MDD in vmPFC (p-adj = 6.45E-05 to 0.02). Enrichment analysis revealed that inflammatory and immune-related pathways were overrepresented (p-adj < 0.05) among the 43 genes in RNAAgeCalc that were also at least nominally associated with PTSD/MDD in vmPFC relative to the 448 RNAAgeCalc genes. Endothelial and mural cells were negatively associated with RNA age residuals in vmPFC (both p-adj = 0.028) and with PTSD/MDD (both p-adj = 0.017).
Conclusions: Results highlight the importance of inflammation and immune system dysregulation in the link between psychopathology and accelerated cellular aging and raise the possibility that blood-brain barrier degradation may play an important role in stress-related accelerated brain aging.
Keywords: PTSD; RNA; accelerated aging; inflammation; major depression; transcriptomic age.
Published 2022. This article is a U.S. Government work and is in the public domain in the USA.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest
Dr. Wolf owns stock in Illumina, Inc. All other named authors report no financial or other conflicts of interest in relationship to the contents of this article.
Figures
References
-
- Benjamini Y, & Hochberg Y (1995). Controlling the False Discovery Rate: A Practical and Powerful Approach to Multiple Testing. Journal of the Royal Statistical Society: Series B (Methodological), 57(1). 10.1111/j.2517-6161.1995.tb02031.x - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

