A perspective of fluorescence microscopy for cellular structural biology with EGFR as witness
- PMID: 36282005
- PMCID: PMC10952613
- DOI: 10.1111/jmi.13151
A perspective of fluorescence microscopy for cellular structural biology with EGFR as witness
Abstract
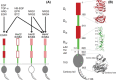
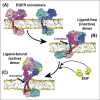
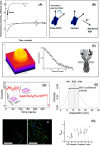
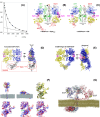
The epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) is a poster child for the understanding of receptor behaviour, and of paramount importance to cell function and human health. Cloned almost forty years ago, the interest in EGFR's structure/function relationships remains unabated, not least because changes in oncogenic EGFR mutants are key drivers of the formation of lung and brain tumours. The structure of the assemblies formed by EGFR have been comprehensibly investigated by techniques such as high-resolution X-ray crystallography, NMR and all-atom molecular dynamics (MD) simulations. However, the complexity embedded in the portfolio of EGFR states that are only possible in the physiological environment of cells has often proved refractory to cell-free structural methods. Conversely, some key inroads made by quantitative fluorescence microscopy and super-resolution have depended on exploiting the wealth of structures available. Here, a brief personal perspective is provided on how quantitative fluorescence microscopy and super-resolution methods have cross-fertilised with cell-free-derived EGFR structural information. I primarily discuss areas in which my research group has made a contribution to fill gaps in EGFR's cellular structural biology and towards developing new tools to investigate macromolecular assemblies in cells.
Keywords: EGFR; FLIM-FRET; microscopy; single molecule; super-resolution.
© 2022 The Authors. Journal of Microscopy published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd on behalf of Royal Microscopical Society.
Figures

References
-
- Low‐Nam, S. T. , Lidke, K. A. , Cutler, P. J. , Roovers, R. C. , Van Bergen En Henegouwen, P. M. P. , Wilson, B. S. , & Lidke, D. S. (2011). ErbB1 dimerization is promoted by domain co‐confinement and stabilized by ligand binding. Nature Structural & Molecular Biology, 18, 1244–1249. 10.1038/nsmb.2135 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Kaplan, M. , Narasimhan, S. , De Heus, C. , Mance, D. , Van Doorn, S. , Houben, K. , Popov‐Čeleketić, D. , Damman, R. , Katrukha, E. A. , Jain, P. , Geerts, W. , Heck, A. , Folkers, G. E. , Kapitein, L. C. , Lemeer, S. , van Bergen En Henegouwen, P. , & Baldus, M. (2016). EGFR dynamics change during activation in native membranes as revealed by NMR. Cell, 167, 1241–51e11. 10.1016/j.cell.2016.10.038 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Huang, Y. , Bharill, S. , Karandur, D. , Peterson, S. M. , Marita, M. , Shi, X. , Shi, X. , Kaliszewski, M. J. , Smith, A. W. , Isacoff, E. Y. , & Kuriyan, J. (2016). Molecular basis for multimerization in the activation of the epidermal growth factor receptor. Elife, 5, 10.7554/eLife.14107 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Needham, S. R. , Hirsch, M. , Rolfe, D. J. , Clarke, D. T. , Zanetti‐Domingues, L. C. , Wareham, R. , & Martin‐Fernandez, M. L. (2013). Measuring EGFR separations on cells with ∼10 nm resolution via fluorophore localization imaging with photobleaching. Plos One, 8, e62331. 10.1371/journal.pone.0062331 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- BB/C51464X/1/BB_/Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council/United Kingdom
- BB/E000215/1/BB_/Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council/United Kingdom
- BB/G006911/1/BB_/Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council/United Kingdom
- BB/L014327/1/BB_/Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council/United Kingdom
- BB/S019553/1/BB_/Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council/United Kingdom
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

