Investigating the Streptococcus sinensis competence regulon through a combination of transcriptome analysis and phenotypic evaluation
- PMID: 36282148
- PMCID: PMC10233337
- DOI: 10.1099/mic.0.001256
Investigating the Streptococcus sinensis competence regulon through a combination of transcriptome analysis and phenotypic evaluation
Abstract
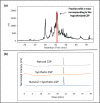
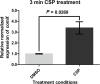
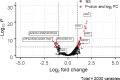
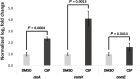
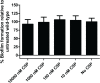
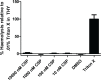
Streptococcus sinensis is a recently identified member of the Mitis group of streptococci. This species has been associated with infective endocarditis; however its mechanisms of pathogenesis and virulence are not fully understood. This study aimed to investigate the influence of the competence-stimulating peptide (CSP) and the competence regulon quorum-sensing circuitry (ComABCDE) on subsequent gene transcription and expression, as well as resultant phenotypes. In this study we confirmed the native CSP identity, ascertained when endogenous CSP was produced and completed a transcriptome-wide analysis of all genes following CSP exposure. RNA sequencing analysis revealed the upregulation of genes known to be associated with competence, biofilm formation and virulence. As such, a variety of phenotypic assays were utilized to assess the correlation between increased mRNA expression and potential phenotype response, ultimately gaining insight into the effects of CSP on both gene expression and developed phenotypes. The results indicated that the addition of exogenous CSP aided in competence development and successful transformation, yielding an average transformation efficiency comparable to that of other Mitis group streptococci. Additional studies are needed to further delineate the effects of CSP exposure on biofilm formation and virulence. Overall, this study provides novel information regarding S. sinensis and provides a substantial foundation on which this species and its role in disease pathogenesis can be further investigated.
Keywords: Streptococcus sinensis; competence; competence-stimulating peptide; quorum sensing.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest.
Figures

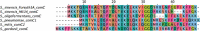

Similar articles
-
Developing multispecies quorum-sensing modulators based on the Streptococcus mitis competence-stimulating peptide.J Biol Chem. 2023 Dec;299(12):105448. doi: 10.1016/j.jbc.2023.105448. Epub 2023 Nov 10. J Biol Chem. 2023. PMID: 37951305 Free PMC article.
-
Elucidating the Role of the Competence Regulon Quorum Sensing Circuitry in Streptococcus cristatus.ACS Chem Biol. 2025 May 16;20(5):1123-1136. doi: 10.1021/acschembio.5c00180. Epub 2025 Apr 21. ACS Chem Biol. 2025. PMID: 40257361
-
Identification of Streptococcus gallolyticus subsp. gallolyticus (Biotype I) Competence-Stimulating Peptide Pheromone.J Bacteriol. 2018 Jun 25;200(14):e00709-17. doi: 10.1128/JB.00709-17. Print 2018 Jul 15. J Bacteriol. 2018. PMID: 29440256 Free PMC article.
-
Quorum sensing in streptococcal biofilm formation.Trends Microbiol. 2005 Jan;13(1):3-6. doi: 10.1016/j.tim.2004.11.009. Trends Microbiol. 2005. PMID: 15639624 Review.
-
Quorum sensing and biofilm formation by Streptococcus mutans.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2008;631:178-88. doi: 10.1007/978-0-387-78885-2_12. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2008. PMID: 18792689 Review.
Cited by
-
Deciphering the Regulatory Role and Molecular Interactions That Drive the Competence Regulon Quorum Sensing Circuitry in Streptococcus constellatus.Biochemistry. 2025 Jul 15;64(14):3104-3113. doi: 10.1021/acs.biochem.5c00195. Epub 2025 Jun 23. Biochemistry. 2025. PMID: 40548891
-
Streptococcus abundance and oral site tropism in humans and non-human primates reflects host and lifestyle differences.NPJ Biofilms Microbiomes. 2025 Jan 17;11(1):19. doi: 10.1038/s41522-024-00642-1. NPJ Biofilms Microbiomes. 2025. PMID: 39824852 Free PMC article.
-
Microbial Musings - Winter 2022.Microbiology (Reading). 2022 Dec;168(12):micro001310. doi: 10.1099/mic.0.001310. Microbiology (Reading). 2022. PMID: 36848206 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

