Phenylacetylglutamine as a novel biomarker of type 2 diabetes with distal symmetric polyneuropathy by metabolomics
- PMID: 36282471
- PMCID: PMC10105673
- DOI: 10.1007/s40618-022-01929-w
Phenylacetylglutamine as a novel biomarker of type 2 diabetes with distal symmetric polyneuropathy by metabolomics
Abstract
Purpose: Type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) with distal symmetric polyneuropathy (DSPN) is a disease involving the nervous system caused by metabolic disorder, while the metabolic spectrum and key metabolites remain poorly defined.
Methods: Plasma samples of 30 healthy controls, 30 T2DM patients, and 60 DSPN patients were subjected to nontargeted metabolomics. Potential biomarkers of DSPN were screened based on univariate and multivariate statistical analyses, ROC curve analysis, and logistic regression. Finally, another 22 patients with T2DM who developed DSPN after follow-up were selected for validation of the new biomarker based on target metabolomics.
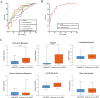
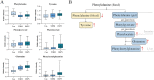
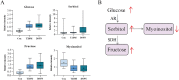
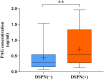
Results: Compared with the control group and the T2DM group, 6 metabolites showed differences in the DSPN group (P < 0.05; FDR < 0.1; VIP > 1) and a rising step trend was observed. Among them, phenylacetylglutamine (PAG) and sorbitol displayed an excellent discriminatory ability and associated with disease severity. The verification results demonstrated that when T2DM progressed to DSPN, the phenylacetylglutamine content increased significantly (P = 0.004).
Conclusion: The discovered and verified endogenous metabolite PAG may be a novel potential biomarker of DSPN and involved in the disease pathogenesis.
Keywords: Biomarker; Distal symmetric polyneuropathy; Metabolomics; Phenylacetylglutamine; Type 2 diabetes.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
All authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- Ismail-Beigi F, Craven T, Banerji MA, Basile J, Calles J, Cohen RM, Cuddihy R, Cushman WC, Genuth S, et al. Effect of intensive treatment of hyperglycaemia on microvascular outcomes in type 2 diabetes: an analysis of the ACCORD randomised trial. Lancet. 2010;376(9739):419–430. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(10)60576-4. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

