GATOR2-dependent mTORC1 activity is a therapeutic vulnerability in FOXO1 fusion-positive rhabdomyosarcoma
- PMID: 36282590
- PMCID: PMC9746907
- DOI: 10.1172/jci.insight.162207
GATOR2-dependent mTORC1 activity is a therapeutic vulnerability in FOXO1 fusion-positive rhabdomyosarcoma
Abstract
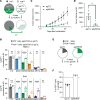
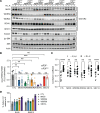
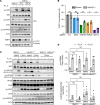
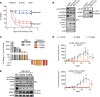
Oncogenic FOXO1 gene fusions drive a subset of rhabdomyosarcoma (RMS) with poor survival; to date, these cancer drivers are therapeutically intractable. To identify new therapies for this disease, we undertook an isogenic CRISPR-interference screen to define PAX3-FOXO1-specific genetic dependencies and identified genes in the GATOR2 complex. GATOR2 loss in RMS abrogated aa-induced lysosomal localization of mTORC1 and consequent downstream signaling, slowing G1-S cell cycle transition. In vivo suppression of GATOR2 impaired the growth of tumor xenografts and favored the outgrowth of cells lacking PAX3-FOXO1. Loss of a subset of GATOR2 members can be compensated by direct genetic activation of mTORC1. RAS mutations are also sufficient to decouple mTORC1 activation from GATOR2, and indeed, fusion-negative RMS harboring such mutations exhibit aa-independent mTORC1 activity. A bisteric, mTORC1-selective small molecule induced tumor regressions in fusion-positive patient-derived tumor xenografts. These findings highlight a vulnerability in FOXO1 fusion-positive RMS and provide rationale for the clinical evaluation of bisteric mTORC1 inhibitors, currently in phase I testing, to treat this disease. Isogenic genetic screens can, thus, identify potentially exploitable vulnerabilities in fusion-driven pediatric cancers that otherwise remain mostly undruggable.
Keywords: Cancer; Drug therapy; Genetics; Oncology; Signal transduction.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


References
-
- Gryder BE, et al. PAX3-FOXO1 establishes myogenic super enhancers and confers BET bromodomain vulnerability. Cancer Discov. 2017;7(8):884–899. doi: 10.1158/2159-8290.CD-16-1297. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

