Combination of the STING Agonist MIW815 (ADU-S100) and PD-1 Inhibitor Spartalizumab in Advanced/Metastatic Solid Tumors or Lymphomas: An Open-Label, Multicenter, Phase Ib Study
- PMID: 36282874
- PMCID: PMC11188043
- DOI: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-22-2235
Combination of the STING Agonist MIW815 (ADU-S100) and PD-1 Inhibitor Spartalizumab in Advanced/Metastatic Solid Tumors or Lymphomas: An Open-Label, Multicenter, Phase Ib Study
Abstract
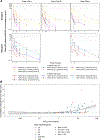
Purpose: The stimulator of IFN genes (STING) is a transmembrane protein that plays a role in the immune response to tumors. Single-agent STING agonist MIW815 (ADU-S100) has demonstrated immune activation but limited antitumor activity. This phase Ib, multicenter, dose-escalation study assessed the safety and tolerability of MIW815 plus spartalizumab (PDR001), a humanized IgG4 antibody against PD-1, in 106 patients with advanced solid tumors or lymphomas.
Patients and methods: Patients were treated with weekly intratumoral injections of MIW815 (50-3,200 μg) on a 3-weeks-on/1-week-off schedule or once every 4 weeks, plus a fixed dose of spartalizumab (400 mg) intravenously every 4 weeks.
Results: Common adverse events were pyrexia (n = 23; 22%), injection site pain (n = 21; 20%), and diarrhea (n = 12; 11%). Overall response rate was 10.4%. The MTD was not reached. Pharmacodynamic biomarker analysis demonstrated on-target activity.
Conclusions: The combination of MIW815 and spartalizumab was well tolerated in patients with advanced/metastatic cancers, including in patients with anti-PD-1 refractory disease. Minimal antitumor responses were seen.
©2022 American Association for Cancer Research.
Figures


References
-
- Barber GN. STING-dependent cytosolic DNA sensing pathways. Trends Immunol 2014;35:88–93. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

