Nucleoside transporters and immunosuppressive adenosine signaling in the tumor microenvironment: Potential therapeutic opportunities
- PMID: 36283452
- PMCID: PMC10290419
- DOI: 10.1016/j.pharmthera.2022.108300
Nucleoside transporters and immunosuppressive adenosine signaling in the tumor microenvironment: Potential therapeutic opportunities
Abstract
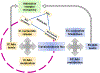
Adenosine compartmentalization has a profound impact on immune cell function by regulating adenosine localization and, therefore, extracellular signaling capabilities, which suppresses immune cell function in the tumor microenvironment. Nucleoside transporters, responsible for the translocation and cellular compartmentalization of hydrophilic adenosine, represent an understudied yet crucial component of adenosine disposition in the tumor microenvironment. In this review article, we will summarize what is known regarding nucleoside transporter's function within the purinome in relation to currently devised points of intervention (i.e., ectonucleotidases, adenosine receptors) for cancer immunotherapy, alterations in nucleoside transporter expression reported in cancer, and potential avenues for targeting of nucleoside transporters for the desired modulation of adenosine compartmentalization and action. Further, we put forward that nucleoside transporters are an unexplored therapeutic opportunity, and modulation of nucleoside transport processes could attenuate the pathogenic buildup of immunosuppressive adenosine in solid tumors, particularly those enriched with nucleoside transport proteins.
Keywords: Adenosine; Drug; Immunosuppression; Nucleoside; Receptor; Signaling; Transporter.
Published by Elsevier Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of Competing Interest The authors declare no potential conflict of interests.
Figures


References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

