Mechanisms Underlying the Differences in the Pharmacokinetics of Six Active Constituents of Huangqi Liuyi Decoction between Normal and Diabetic Nephropathy Mouse Models
- PMID: 36285162
- PMCID: PMC9588345
- DOI: 10.1155/2022/2481654
Mechanisms Underlying the Differences in the Pharmacokinetics of Six Active Constituents of Huangqi Liuyi Decoction between Normal and Diabetic Nephropathy Mouse Models
Abstract
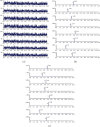
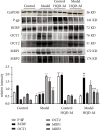
The aim of this study was to explore the mechanisms underlying the differences in the pharmacokinetics of Huangqi Liuyi decoction extract (HQD) under physiological and pathological conditions. The roles of liver cytochrome P450 metabolic enzymes (Cyp450) and small intestinal transporters were also investigated. The cocktail probe drug method was used to investigate the effects of diabetic nephropathy (DN) and HQD on metabolic enzyme activity. The expression levels of liver Cyp450 metabolic enzymes (Cyp1A2, Cyp2C37, Cyp3A11, Cyp2E1, and Cyp2C11) and small intestinal transporters (breast cancer resistance protein (BCRP), P-glycoprotein (P-gp), organic cation transporters (OCTs), and multidrug resistance-associated protein (MRPs) were determined using western blot. Compared to normal mice, the expression of OCT1, OCT2, MRP1, and MRP2 was increased in DN mice, while that of P-gp and BCRP (P < 0.05 and P < 0.001) was inhibited. HQD inhibited expression of Cyp1A2 and Cyp3A11 and increased the expression of P-gp and BCRP in normal mice. In DN mice, HQD induced expression of BCRP and inhibited expression of Cyp2C37, Cyp3A11, OCT2, MRP1, and MRP2. The activity of each Cyp450 enzyme was consistent with changes in expression. The changes in pharmacokinetic parameters of HQD in DN might, in part, be secondary to decreased expression of P-gp and BCRP. HQD varied in regulating transporter activities between health and disease. These findings support careful application of HQD-based treatment in DN, especially in combination with other drugs.
Copyright © 2022 Qun Wang et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Study on the liver Drug's dominant metabolic enzymes for six effective components of the Huang qi Liuyi decoction.Front Pharmacol. 2023 Apr 14;14:1175896. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2023.1175896. eCollection 2023. Front Pharmacol. 2023. PMID: 37124208 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of Huangqi Liuyi Decoction in the Treatment of Diabetic Nephropathy and Tissue Distribution Difference of its Six Active Constituents Between Normal and Diabetic Nephropathy Mouse Models.Front Pharmacol. 2022 Jun 21;13:934720. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.934720. eCollection 2022. Front Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 35800436 Free PMC article.
-
Pharmacokinetic Difference of Six Active Constituents of Huangqi Liuyi Decoction between Control and Diabetic Nephropathy Mouse Models.Int J Anal Chem. 2022 May 25;2022:7602992. doi: 10.1155/2022/7602992. eCollection 2022. Int J Anal Chem. 2022. PMID: 35663235 Free PMC article.
-
Imbalance of Drug Transporter-CYP450s Interplay by Diabetes and Its Clinical Significance.Pharmaceutics. 2020 Apr 11;12(4):348. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics12040348. Pharmaceutics. 2020. PMID: 32290519 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Metabolism and interactions of Ivermectin with human cytochrome P450 enzymes and drug transporters, possible adverse and toxic effects.Arch Toxicol. 2021 May;95(5):1535-1546. doi: 10.1007/s00204-021-03025-z. Epub 2021 Mar 15. Arch Toxicol. 2021. PMID: 33719007 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Study on the liver Drug's dominant metabolic enzymes for six effective components of the Huang qi Liuyi decoction.Front Pharmacol. 2023 Apr 14;14:1175896. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2023.1175896. eCollection 2023. Front Pharmacol. 2023. PMID: 37124208 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

