Recent Advances in Macroporous Hydrogels for Cell Behavior and Tissue Engineering
- PMID: 36286107
- PMCID: PMC9601978
- DOI: 10.3390/gels8100606
Recent Advances in Macroporous Hydrogels for Cell Behavior and Tissue Engineering
Abstract
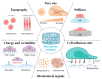
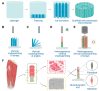
Hydrogels have been extensively used as scaffolds in tissue engineering for cell adhesion, proliferation, migration, and differentiation because of their high-water content and biocompatibility similarity to the extracellular matrix. However, submicron or nanosized pore networks within hydrogels severely limit cell survival and tissue regeneration. In recent years, the application of macroporous hydrogels in tissue engineering has received considerable attention. The macroporous structure not only facilitates nutrient transportation and metabolite discharge but also provides more space for cell behavior and tissue formation. Several strategies for creating and functionalizing macroporous hydrogels have been reported. This review began with an overview of the advantages and challenges of macroporous hydrogels in the regulation of cellular behavior. In addition, advanced methods for the preparation of macroporous hydrogels to modulate cellular behavior were discussed. Finally, future research in related fields was discussed.
Keywords: biochemical cues; cell behaviors; macroporous hydrogels; matrix mechanics; tissue engineering.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures






Similar articles
-
Macroporous Hydrogel Scaffolds for Three-Dimensional Cell Culture and Tissue Engineering.Tissue Eng Part B Rev. 2017 Oct;23(5):451-461. doi: 10.1089/ten.TEB.2016.0465. Epub 2017 Feb 3. Tissue Eng Part B Rev. 2017. PMID: 28067115 Review.
-
Emulsion-Templated Gelatin/Amino Acids/Chitosan Macroporous Hydrogels with Adjustable Internal Dimensions for Three-Dimensional Stem Cell Culture.ACS Biomater Sci Eng. 2024 Aug 12;10(8):4878-4890. doi: 10.1021/acsbiomaterials.4c00501. Epub 2024 Jul 23. ACS Biomater Sci Eng. 2024. PMID: 39041681
-
Construction of Injectable Self-Healing Macroporous Hydrogels via a Template-Free Method for Tissue Engineering and Drug Delivery.ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2018 Oct 31;10(43):36721-36732. doi: 10.1021/acsami.8b13077. Epub 2018 Oct 18. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2018. PMID: 30261143
-
Macroporous methacrylated hyaluronic acid hydrogel with different pore sizes forin vitroandin vivoevaluation of vascularization.Biomed Mater. 2022 Jan 25;17(2). doi: 10.1088/1748-605X/ac494b. Biomed Mater. 2022. PMID: 34996058
-
Structured Macroporous Hydrogels: Progress, Challenges, and Opportunities.Adv Healthc Mater. 2018 Jan;7(1). doi: 10.1002/adhm.201700927. Epub 2017 Dec 1. Adv Healthc Mater. 2018. PMID: 29195022 Review.
Cited by
-
3D bioprinted piezoelectric hydrogel synergized with LIPUS to promote bone regeneration.Mater Today Bio. 2025 Feb 21;31:101604. doi: 10.1016/j.mtbio.2025.101604. eCollection 2025 Apr. Mater Today Bio. 2025. PMID: 40066077 Free PMC article.
-
Injectable Hydrogels for Nervous Tissue Repair-A Brief Review.Gels. 2024 Mar 9;10(3):190. doi: 10.3390/gels10030190. Gels. 2024. PMID: 38534608 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Semi-Interpenetrating Polymer Networks Based on Hydroxy-Ethyl Methacrylate and Poly(4-vinylpyridine)/Polybetaines, as Supports for Sorption and Release of Tetracycline.Polymers (Basel). 2023 Jan 17;15(3):490. doi: 10.3390/polym15030490. Polymers (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36771791 Free PMC article.
-
Juniper Berry Oil as a Functional Additive in Chitosan-Water Kefiran-Paramylon Porous Sponges: Structural, Physicochemical, and Protein Interaction Insights.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 May 31;26(11):5314. doi: 10.3390/ijms26115314. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40508122 Free PMC article.
-
Porous Hydrogels for Immunomodulatory Applications.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 May 9;25(10):5152. doi: 10.3390/ijms25105152. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38791191 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Hussey G.S., Dziki J.L., Badylak S.F. Extracellular matrix-based materials for regenerative medicine. Nat. Rev. Mater. 2018;3:159–173. doi: 10.1038/s41578-018-0023-x. - DOI
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

