Formulation and Evaluation of Diclofenac Potassium Gel in Sports Injuries with and without Phonophoresis
- PMID: 36286113
- PMCID: PMC9601609
- DOI: 10.3390/gels8100612
Formulation and Evaluation of Diclofenac Potassium Gel in Sports Injuries with and without Phonophoresis
Abstract
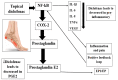
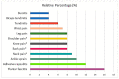
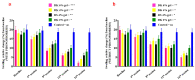
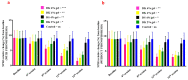
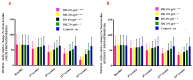
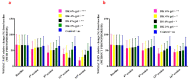
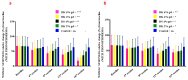
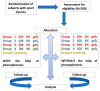
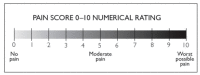
Background: Pain remains a global public heath priority. Phonophoresis, also known as sonophoresis or ultrasonophoresis, is when an ultrasound is used to maximize the effects of a topical drug. Purpose: The objective of this study was to test, in patients injured in sports or accidents (N = 200), the efficacy of diclofenac potassium (DK) 6%, 4%, and 2% formulated gels with and without phonophoresis in comparison with market available standard diclofenac sodium (DS or DN) gel. Methods: The patients were enrolled after informed consent. By using the lottery method, 100 patients were randomly segregated into five groups without phonophoresis and repeated similarly with phonophoresis at a frequency of 0.8 MHz, an intensity of about 1.5 W/cm2, and at continuous mode (2:1). Group-1 was treated with 6% DK gel, group-2 was treated with 4% DK gel, group-3 was treated with 2% DK gel, group-4 was treated with 4% DS gel and group-5 was given control gel three to four times a week for 4 weeks. The patients were screened by using NPRS and WOMAC scales. They were assessed on the baseline, 4th session, 8th session, 12th session, and 16th session. Results: Significant dose-dependently relief was observed in NPRS (Numeric Pain Rating Scale) and the WOMAC (Western Ontario McMaster Osteo-Arthritis) index for pain in disability and stiffness for each group treated with DK gel compared to DS gel. Phonophoresis increased these benefits significantly when used after topical application of DK gel or DS gel, and the dose-dependent effects of DK gel plus phonophoresis were stronger than the dose-dependent effects of DS gel plus phonophoresis. The faster and profounder relief was due to phonophoresis, which allows more penetration of the DK gel into the skin as compared to the direct application of DK gel in acute, uncomplicated soft tissue injury, such as plantar fasciitis, bursitis stress injuries, and tendinitis. In addition, DK gel with phonophoresis was well tolerated. Thus, in this personalized clinical setting, according to the degree of inflammation or injured-induced pain, disability, and stiffness, DK gel 6% with phonophoresis appeared more effective and thus more recommendable than DS gel 6% alone or DS gel 6% combined to phonophoresis.
Keywords: diclofenac potassium gel; diclofenac sodium gel; pain; phonophoresis; sport injuries.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Evaluation of polyherbal gel for musculoskeletal injuries in industrial workers.Work. 2024;78(2):447-460. doi: 10.3233/WOR-230178. Work. 2024. PMID: 38251085 Clinical Trial.
-
Efficacy and mechanism of Jasminum sambac gel for musculoskeletal injuries.Am J Transl Res. 2024 May 15;16(5):1587-1601. doi: 10.62347/VMJO7002. eCollection 2024. Am J Transl Res. 2024. PMID: 38883366 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of the Efficacy of Different Concentrations of Diclofenac Sodium Phonophoresis (1.16% vs 2.32%) in Patients with Knee Osteoarthritis: a Randomized Double-Blind Controlled Trial.Acta Chir Orthop Traumatol Cech. 2021;88(2):117-123. Acta Chir Orthop Traumatol Cech. 2021. PMID: 33960924 Clinical Trial. English.
-
Effects of therapeutic ultrasound for knee osteoarthritis: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Clin Rehabil. 2019 Dec;33(12):1863-1875. doi: 10.1177/0269215519866494. Epub 2019 Aug 5. Clin Rehabil. 2019. PMID: 31382781
-
The effect of ultrasound or phonophoresis as an adjuvant treatment for non-specific neck pain: systematic review of randomised controlled trials.Disabil Rehabil. 2022 Jun;44(13):2968-2974. doi: 10.1080/09638288.2020.1851785. Epub 2020 Nov 30. Disabil Rehabil. 2022. PMID: 33253599
Cited by
-
Effect of laxative polyherbal paste for loperamide induced constipation in rats.Am J Transl Res. 2024 Sep 15;16(9):4714-4727. doi: 10.62347/XSFH4004. eCollection 2024. Am J Transl Res. 2024. PMID: 39398568 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical Practice Guidelines for Topical NSAIDs in the Treatment of Sports Injuries.J Evid Based Med. 2025 Mar;18(1):e12661. doi: 10.1111/jebm.12661. Epub 2025 Jan 10. J Evid Based Med. 2025. PMID: 39791352 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical Diathermy Performance Evaluation of Multi-hour Sustained Acoustic Medicine Treatment with 2.5% Diclofenac Ultrasound Coupling Patch.Int J Phys Med Rehabil. 2023;11(6):678. Epub 2023 Jun 20. Int J Phys Med Rehabil. 2023. PMID: 37692795 Free PMC article.
-
Phytochemical, antioxidant, antipyretic and anti-inflammatory activities of aqueous-methanolic leaf extract of Mangifera indica.Am J Transl Res. 2023 Jul 15;15(7):4533-4543. eCollection 2023. Am J Transl Res. 2023. PMID: 37560231 Free PMC article.
-
Alternatives to Conventional Topical Dosage Forms for Targeted Skin Penetration of Diclofenac Sodium.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Jul 6;25(13):7432. doi: 10.3390/ijms25137432. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39000538 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ivins D. Acute ankle sprain: An update. Am. Fam. Physician. 2006;74:1714–1720. - PubMed
-
- Osteoarthritis: The care and management of osteoarthritis in adults. [(accessed on 24 June 2013)];Inst. Clin. Excell. Clin. Guidel. 2008 Available online: http://guidance.nice.org.uk/CG59.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

