Characterization of Sugar Reduction in Model Confectionary Gels Using Descriptive Analysis
- PMID: 36286145
- PMCID: PMC9601666
- DOI: 10.3390/gels8100644
Characterization of Sugar Reduction in Model Confectionary Gels Using Descriptive Analysis
Abstract
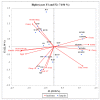
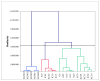
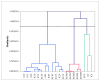
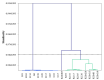
Successful sugar reduction in food products mimics the sensory and functional properties of the full sugar counterpart. The initial step of sugar reduction is to determine how the absence of sugar affects these properties. Descriptive analysis was conducted on four gel types (gelatin, ι-carrageenan, κ-carrageenan, and konjac glucomannan) and a range of sugar concentrations from 0-20% w/v to create a sensory profile of model confectionary gels for comparison to instrumental texture profile analysis data. The sensory descriptive data were analyzed using analysis of variance and principal component analysis. Correlation analysis, cluster analysis, and partial least squares regression (PLS-R) were used to compare and correlate sensory and instrumental data. Regardless of sugar concentration, sensory analysis primarily clustered samples by gelling agent type, such as in the case of konjac glucomannan consistently being characterized as chewy. Cohesion and gumminess were correlated highly with melt-in-mouth and a jiggly texture, while adhesion and fracturability were negatively correlated. In the PLS-R samples biplot, gelatin and iota carrageenan samples were located near these attributes indicating their aptness as descriptors. In conclusion, descriptive analysis provided a more discriminating method for characterizing model confectionary gels.
Keywords: carrageenan; descriptive analysis; gelatin; konjac glucomannan; sugar reduction.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Milner L., Kerry J.P., O’Sullivan M.G., Gallagher E. Physical, textural and sensory characteristics of reduced sucrose cakes, incorporated with clean-label sugar-replacing alternative ingredients. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2020;59:102235. doi: 10.1016/j.ifset.2019.102235. - DOI
-
- Riedel R., Böhme B., Rohm H. Development of formulations for reduced-sugar and sugar-free agar-based fruit jellies. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2015;50:1338–1344. doi: 10.1111/ijfs.12787. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

