Progress in Composite Hydrogels and Scaffolds Enriched with Icariin for Osteochondral Defect Healing
- PMID: 36286148
- PMCID: PMC9602414
- DOI: 10.3390/gels8100648
Progress in Composite Hydrogels and Scaffolds Enriched with Icariin for Osteochondral Defect Healing
Abstract
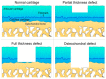
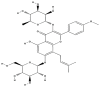
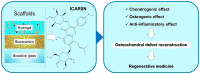
Osteochondral structure reconstruction by tissue engineering, a challenge in regenerative medicine, requires a scaffold that ensures both articular cartilage and subchondral bone remodeling. Functional hydrogels and scaffolds present a strategy for the controlled delivery of signaling molecules (growth factors and therapeutic drugs) and are considered a promising therapeutic approach. Icariin is a pharmacologically-active small molecule of prenylated flavonol glycoside and the main bioactive flavonoid isolated from Epimedium spp. The in vitro and in vivo testing of icariin showed chondrogenic and ostseoinductive effects, comparable to bone morphogenetic proteins, and suggested its use as an alternative to growth factors, representing a low-cost, promising approach for osteochondral regeneration. This paper reviews the complex structure of the osteochondral tissue, underlining the main aspects of osteochondral defects and those specifically occurring in osteoarthritis. The significance of icariin's structure and the extraction methods were emphasized. Studies revealing the valuable chondrogenic and osteogenic effects of icariin for osteochondral restoration were also reviewed. The review highlighted th recent state-of-the-art related to hydrogels and scaffolds enriched with icariin developed as biocompatible materials for osteochondral regeneration strategies.
Keywords: bone morphogenetic proteins; cartilage; flavonoids; hydrogel; osteoarthritis; osteochondral defect.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Sacitharan P.K. Ageing and osteoarthritis. In: Harris J., Korolchuk V., editors. Biochemistry and Cell Biology of Ageing: Part II Clinical Science. Subcellular Biochemistry. Springer; Singapore: 2019. pp. 123–159. - PubMed
-
- He L., He T., Xing J., Zhou Q., Fan L., Liu C., Chen Y., Wu D., Tian Z., Liu B., et al. Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes protect cartilage damage and relieve knee osteoarthritis pain in a rat model of osteoarthritis. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2020;11:276. doi: 10.1186/s13287-020-01781-w. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

