Characterization of Acid- and Pepsin-Soluble Collagen Extracted from the Skin of Purple-Spotted Bigeye Snapper
- PMID: 36286166
- PMCID: PMC9602141
- DOI: 10.3390/gels8100665
Characterization of Acid- and Pepsin-Soluble Collagen Extracted from the Skin of Purple-Spotted Bigeye Snapper
Abstract
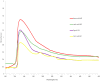
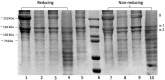
Fish processing waste is a prospective source of collagen and a cost-effective environmental pollutant. The skin of the purple-spotted bigeye snapper (Priacanthus tayenus) was extracted utilising various acid soluble collagens (ASC) including acetic acid (AAC), lactic acid (LAC), citric acid (CAC) and pepsin soluble collagens (PSC). In this study, PSC (6.65%) had the highest collagen yield, followed by AAC (5.79%), CAC (4.15%), and LAC (3.19%). The maximum temperatures (Tmax) denaturation of AAC, LAC, CAC, and PSC were 31.4, 31.7, 31.5, and 33.2 °C, respectively. UV-VIS absorption spectra showed all extracted collagens had a range of absorbance at 230 nm, due to the presence of glycine, proline, hydroxyproline, and triple-helical collagen. Additionally, they exhibited amide A, B, amide I, II, and III peaks. SDS−PAGE identified all extracted collagens as type I. The PSC had a significantly higher (p < 0.05) hydroxyproline content than acidic extraction 66.3 ± 1.03 (mg/g sample). Furthermore, all samples were extremely soluble in acetic conditions at pH 5, and all collagen was soluble in NaCl up to 3% (w/v). Therefore, PSC was the best treatment since it did not impact collagen triple helical and acetic acid yielded the most collagen in ASC extraction. Overall, the analysis revealed that fish skin waste might be used as an alternate source of collagen in diverse applications, particularly in food applications.
Keywords: characterization; collagen; extraction; fish processing waste; skin purple-spotted bigeye snapper (Priacanthus tayenus).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Huda N., Seow E.K., Normawati M.N., Nik Aisyah N.M., Fazilah A., Easa A.M. Effect of duck feet collagen addition on physicochemical properties of surimi. Int. Food Res. J. 2013;20:537–544.
-
- Oslan S.N.H., Li C.X., Shapawi R., Mokhtar R.A.M., Noordin W.N.M., Huda N. Extraction and characterization of bioactive fish by-product collagen as promising for potential wound healing agent in pharmaceutical applications: Current trend and future perspective. Int. J. Food Sci. 2022;2022:9437878. doi: 10.1155/2022/9437878. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Huda N., Seow E.K., Normawati M.N., Nik Aisyah N.M., Fazilah A., Easa A.M. Preliminary study on physicochemical properties of duck feet Collagen. Int. J. Poult. Sci. 2013;12:615–621. doi: 10.3923/ijps.2013.615.621. - DOI
-
- Nik Muhammad N.A., Huda N., Karim A.A., Abdorreza M.N. Effects of acid type extraction on characterization and sensory profile of duck feet gelatin: Towards finding bovine gelatin alternative. J. Food Meas. Charact. 2018;12:480–486. doi: 10.1007/s11694-017-9661-8. - DOI
-
- Gao R., Yu Q., Shen Y., Chu Q., Chen G., Fen S., Yang M., Yuan L., Clements D.J.M., Sun Q. Production, bioactive properties, and potential applications of fish protein hydrolysates: Developments and challenges. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2021;110:687–699. doi: 10.1016/j.tifs.2021.02.031. - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

