Novel Silica Hybrid Xerogels Prepared by Co-Condensation of TEOS and ClPhTEOS: A Chemical and Morphological Study
- PMID: 36286178
- PMCID: PMC9601464
- DOI: 10.3390/gels8100677
Novel Silica Hybrid Xerogels Prepared by Co-Condensation of TEOS and ClPhTEOS: A Chemical and Morphological Study
Abstract
The search for new materials with improved properties for advanced applications is, nowadays, one of the most relevant and booming fields for scientists due to the environmental and technological needs of our society. Within this demand, hybrid siliceous materials, made out of organic and inorganic species (ORMOSILs), have emerged as an alternative with endless chemical and textural possibilities by incorporating in their structure the properties of inorganic compounds (i.e., mechanical, thermal, and structural stability) in synergy with those of organic compounds (functionality and flexibility), and thus, bestowing the material with unique properties, which allow access to multiple applications. In this work, synthesis using the sol-gel method of a series of new hybrid materials prepared by the co-condensation of tetraethoxysilane (TEOS) and 4-chlorophenyltriethoxysilane (ClPhTEOS) in different molar ratios is described. The aim of the study is not only the preparation of new materials but also their characterization by means of different techniques (FT-IR, 29Si NMR, X-ray Diffraction, and N2/CO2 adsorption, among others) to obtain information on their chemical behavior and porous structure. Understanding how the chemical and textural properties of these materials are modulated with respect to the molar percentage of organic precursor will help to envisage their possible applications: From the most conventional such as catalysis, adsorption, or separation, to the most advanced in nanotechnology such as microelectronics, photoluminescence, non-linear optics, or sensorics.
Keywords: ORMOSILs; TEOS; chemical-textural properties; chlorophenyltriethoxysilane; hybrid materials; ordered structures; silica species; xerogels.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


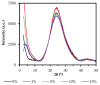
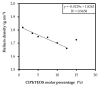

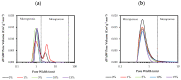

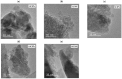
Similar articles
-
Tunability of Hybrid Silica Xerogels: Surface Chemistry and Porous Texture Based on the Aromatic Precursor.Gels. 2023 May 5;9(5):382. doi: 10.3390/gels9050382. Gels. 2023. PMID: 37232974 Free PMC article.
-
Novel Organochlorinated Xerogels: From Microporous Materials to Ordered Domains.Polymers (Basel). 2021 Apr 27;13(9):1415. doi: 10.3390/polym13091415. Polymers (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33925564 Free PMC article.
-
Hybrid Xerogels: Study of the Sol-Gel Process and Local Structure by Vibrational Spectroscopy.Polymers (Basel). 2021 Jun 24;13(13):2082. doi: 10.3390/polym13132082. Polymers (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34202735 Free PMC article.
-
Silicone-Based Organic-Inorganic Hybrid Aerogels and Xerogels.Chemistry. 2017 Apr 19;23(22):5176-5187. doi: 10.1002/chem.201603680. Epub 2017 Jan 20. Chemistry. 2017. PMID: 28105748 Review.
-
Chitosan bio-based organic-inorganic hybrid aerogel microspheres.Chemistry. 2012 Jul 2;18(27):8264-77. doi: 10.1002/chem.201104006. Epub 2012 Jun 11. Chemistry. 2012. PMID: 22689451 Review.
Cited by
-
The Methyl Functionality of Monolithic Silica Xerogels Synthesized via the Co-Gelation Approach Combined with Surface Silylation.Gels. 2022 Dec 30;9(1):33. doi: 10.3390/gels9010033. Gels. 2022. PMID: 36661800 Free PMC article.
-
Tunability of Hybrid Silica Xerogels: Surface Chemistry and Porous Texture Based on the Aromatic Precursor.Gels. 2023 May 5;9(5):382. doi: 10.3390/gels9050382. Gels. 2023. PMID: 37232974 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Hannachi Y., Hafidh A., Ayed S. Effectiveness of novel xerogels adsorbents for cadmium uptake from aqueous solution in batch and column modes: Synthesis, characterization, equilibrium, and mechanism analysis. Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 2019;143:11–23. doi: 10.1016/j.cherd.2019.01.006. - DOI
-
- Wojciechowska P., Cierpiszewski R. Gelatin—Siloxane Hybrid Monoliths as Novel Heavy Metal Adsorbents. Appl. Sci. 2022;12:1258. doi: 10.3390/app12031258. - DOI
-
- Didó C.A., Coelho F.L., Closs M.B., Deon M., Horowitz F., Bernardi F., Schneider P.H., Benvenutti E. V Strategy to isolate ionic gold sites on silica surface: Increasing their efficiency as catalyst for the formation of 1,3-diynes. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2020;594:117444. doi: 10.1016/j.apcata.2020.117444. - DOI
-
- Estevez R., Luna D., Bautista F.M. Sulfonated organosilica-aluminum phosphates as useful catalysts for acid-catalyzed reactions: Insights into the effect of synthesis parameters on the final catalyst. Catal. Today. 2022;390–391:12–21. doi: 10.1016/j.cattod.2021.12.015. - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

