A phase 2 study of nivolumab combined with ibrutinib in patients with diffuse large B-cell Richter transformation of CLL
- PMID: 36287248
- PMCID: PMC10189379
- DOI: 10.1182/bloodadvances.2022008790
A phase 2 study of nivolumab combined with ibrutinib in patients with diffuse large B-cell Richter transformation of CLL
Abstract
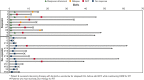
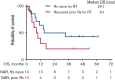
Richter transformation (RT) is a rare complication of chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) that has dismal outcomes. Upregulation of PD-1/PD-L1 drives immunological evasion in patients with RT. We hypothesized that combining nivolumab, a PD-1 blocking antibody, with the BTK inhibitor (BTKi) ibrutinib could potentiate tumor-cell killing. We conducted an investigator-initiated phase 2 clinical trial to assess the efficacy of combined nivolumab and ibrutinib in patients with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) RT and CLL. Patients included were ≥18 years of age with adequate hepatic and renal function. Patients received nivolumab every 2 weeks of a 4-week cycle for a maximum of 24 cycles. A standard dose ibrutinib was initiated from cycle 2 onward and continued daily until progression. For patients who were already on ibrutinib at the time of study entry, the same was continued while nivolumab was initiated. A total of 24 patients with RT with a median age of 64.5 years (range, 47-88) were enrolled. Ten patients (42%) had received prior treatment for RT and 13 patients (54%) had received a prior BTKi. A total of 10 patients (42%) responded with a median duration of response of 15 months. The median overall survival was 13 months. Four of 24 (17%) patients had checkpoint inhibition-related immunological toxicities. In the CLL cohort, 10 patients were enrolled, of whom 3 patients converted from partial to complete remission; 1 patient had a grade 2 immunological toxicity. Combined nivolumab and ibrutinib is an active regimen for patients with DLBCL RT with an overall response rate of 42%. Given the limited treatment options for patients with RT, checkpoint inhibition provides a potential therapeutic option. This trial is registered at www.clinicaltrials.gov as #NCT02420912.
© 2023 by The American Society of Hematology. Licensed under Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0), permitting only noncommercial, nonderivative use with attribution. All other rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict-of-interest disclosure: N.J. has received research support from BMS, Pharmacyclics, AbbVie, Genentech, AstraZeneca, Pfizer, Servier, ADC Therapeutics, Cellectis, Adaptive Biotechnologies, Incyte, Precision Biosciences, Aprea Therapeutics, Fate Therapeutics, Kite/Gilead, Mingsight, Takeda, Medisix, Loxo Oncology, Novalgen, Dialectic Therapeutics, Newave, and TransThera Sciences, and has participated in advisory board meetings and received honoraria from BMS, Pharmacyclics, Janssen, AbbVie, Genentech, AstraZeneca, Adaptive Biotechnologies, Kite/Gilead, Precision Biosciences, Beigene, Cellectis, TG Therapeutics, MEI Pharma, Ipsen, and CareDX. P.T. has received research funding from AbbVie, Pharmacyclics, Lilly, Adaptive Biotechnologies and has participated in advisory boards/consultations with Janssen, AbbVie, Adaptive Biotechnologies, BeiGene, Lilly, and Genentech. A.F. has received research funding from BeiGene and AstraZeneca. J.B. has received honoraria from and participated in advisory boards/consultations with Janssen, has received research funding from AstraZeneca, BeiGene, and Pharmacyclics LLC, an AbbVie company, and has participated in speakers' bureau for and received travel expenses from Gilead, Janssen, Novartis, Pharmacyclics LLC, an AbbVie company, and TG Therapeutics. T.K. has received research grants from Amgen, Ascentage, Astellas, AstraZeneca, BMS, Cellenkos, Pulmotech, and Genfleet; personal fees from Agios, Cure, Daiichi Sankyo, Genzyme, Liberum, Novartis, and Sanofi-Aventis; and research grants and personal fees from AbbVie, Genetech, Jazz Pharmaceuticals, and Pfizer. N.D. has received research funding from Daiichi Sankyo, BMS, Pfizer, Karyopharm, Sevier, Genentech, Astellas, Sobi, Hanmi, Fate, Gilead, Forty-Seven, Trillium, KAHR, Kite, and ImmunoGen and has served in a consulting or advisory role for Daiichi Sankyo, BMS, Pfizer, Syndax, Astellas, Immunogen, Glycostem, Novartis, Celgene, AbbVie, Arch Oncology, Kite, Gilead, Servier, Trillium, Shattuck Labs, and Agios. G.B. has received research funding from AbbVie, Agensys, Arvinas, AstraZeneca, Bayer Healthcare AG, BioLineRx, BMS, Cantargia AB, Cyclacel, Eli Lilly and Company, Esai, GlaxoSmithKline, Incyte, Merck, Novartix, Oncoceutics, Polaris, Tetralogic Pharmaceuticals, and XBiotechUSA and personal fees from Argenx, BioLineRx, BioTheryX, Fate Therapeutics, NKarta, Strategia Therapeutics, and TPC Therapeutic. M. Konopleva received research funding from AbbVie, Genentech, F. Hoffman La-Roche, Eli Lilly, Cellectis, Calithera, Ablynx, Stemline Therapeutics, Agios, Ascentage, AstraZeneca, Rafael Pharmaceutical, Sanofi and Forty-Seven; served as a consultant/advisory board member for AbbVie, Genentech, F. Hoffman La-Roche, Stemline Therapeutics, Amgen, Forty-Seven, Kisoji, and Janssen; and outside the submitted work has a patent US 7795305 B2 CDDO-compounds and combination therapies with royalties paid to Reata Pharm, a patent combination therapy with a mutant IDH1 inhibitor and a BCL-2 inhibitor licensed to Eli Lilly, and a patent 62/993 166 combination of an MCL-1 inhibitor and midostaurin, uses and pharmaceutical compositions thereof, pending to Novartis. N.P. has received research grants from Novartis, Stemline Therapeutics, Samus Therapeutics, AbbVie, Cellectics, Affymetrix/Thermo Fisher Scientific, Daiichi Sankyo, Plexxikon, and MustangBio; honoraria from Incyte, Novartis, LFB Biotechnologies, Stemline Therapeutics, Celgene, AbbVie, MustangBio, Roche Molecular Diagnostics, Blueprint Medicines, DAVA Pharmaceuticals, Springer Science+Business Media LLC, Aptitude Health, NeoPharm, and CareDX; has participated in advisory boards/consultation with Blueprint Medicines, Pacylex Pharmaceuticals Inc, Immunogen, BMS, Clearview Healthcare Partners, Astellas Pharma US Inc., Protagonist Therapeutics, Triptych Health Partners, CTI BioPharma Corp; and received travel/accommodation expenses from Stemline Therapeutics, Celgene, AbbVie, DAVA oncology, and Mustang Bio. H.K. has received research grants and honoraria from AbbVie, Amgen, Ascentage, BMS, Daiichi Sankyo, Immunogen, Jazz, Novartis, Pfizer, and Sanofi, honoraria from Actinium (advisory board), Adaptive Biotechnologies, Aptitude Health, BioAscend, DeltaFly, Janssen Global, Oxford Biomedical, and Takeda Oncology. W.W. participated in advisory boards/consultation with Sanofi; and received research funding from GlaxoSmithKline/Novartis, AbbVie, Genentech, Pharmacyclics, Acerta Pharma, Gilead Sciences, Janssen, Juno Therapeutics, Kite, a Gilead company, Oncternal Therapeutics, Loxo, Xencor, miRagen, Sunesis Pharmaceuticals, and Cyclacel. The remaining authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures



References
-
- Burger JA. Treatment of Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia. N Engl J Med. 2020;383(5):460–473. - PubMed
-
- Hallek M, Al-Sawaf O. Chronic lymphocytic leukemia: 2022 update on diagnostic and therapeutic procedures. Am J Hematol. 2021;96(12):1679–1705. - PubMed
-
- Jain N, Keating MJ. Richter transformation of CLL. Expert Rev Hematol. 2016;9(8):793–801. - PubMed
-
- Rossi D, Spina V, Gaidano G. Biology and treatment of Richter syndrome. Blood. 2018;131(25):2761–2772. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

