Infection with SARS-CoV-2 is associated with menstrual irregularities among women of reproductive age
- PMID: 36288342
- PMCID: PMC9604006
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0276131
Infection with SARS-CoV-2 is associated with menstrual irregularities among women of reproductive age
Abstract
Background: Biological and psychological mechanisms may be responsible for menstrual irregularities occurring among women during the COVID-19 pandemic.
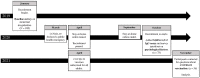
Study design: From January 2019 to September 2021, women (18- to 45-years-old and not using hormonal contraception) were recruited in Miami-Dade County, Florida. Cross-sectional, self-report surveys collected data on menstrual irregularities, COVID-19 vaccination, stress, depression, and loneliness. A EUA approved rapid test assay using whole blood measured SARS-CoV-2 IgG antibodies. Chi-square and Fisher's exact tests described menstrual irregularities among women recruited before versus after the start of the COVID-19 pandemic and with detectable versus undetectable SARS-CoV-2 IgG antibodies. A logistic regression examined the relationship between the presence of SARS-CoV-2 IgG antibodies and menstrual irregularities controlling for age, stress, depression, and loneliness.
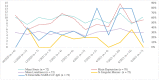
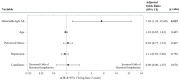
Results: Among 182 women enrolled, 73 were enrolled after pandemic onset, and 36 provided vaccination data. Having detectable SARS-CoV-2 IgG antibodies was associated with a higher percentage of menstrual irregularities among unvaccinated women (0% vs. 39%, p = .026) and among all women regardless of vaccination status (31% vs. 5%; p = .005). Adjusting for age and psychological variables, the odds of menstrual irregularities were 7.03 times (95% CI [1.39, 35.60]; p = .019) higher among women with detectable antibodies compared to women without detectable antibodies. Neither enrollment date, age, nor psychological factors were associated to menstrual irregularities.
Conclusions: Biological mechanisms related to SARS-CoV-2 infection may be responsible for irregular menstruation and should be further examined to mitigate the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on women's health.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
References
-
- World Health Organization. Timeline: WHO’s COVID-19 response. 2021. https://www.who.int/emergencies/diseases/novel-coronavirus-2019/interact...
-
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. COVID Data Tracker. Atlanta, GA: US Department of Health and Human Services, CDC; 2022 Apr. https://covid.cdc.gov/covid-data-tracker
-
- Czeisler MÉ, Lane RI, Wiley JF, Czeisler CA, Howard ME, Rajaratnam SMW. Follow-up survey of US adult reports of mental health, substance use, and suicidal ideation during the COVID-19 pandemic, September 2020. JAMA Netw Open. 2021;4: e2037665. doi: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2020.37665 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

