Epidemiological measures for assessing the dynamics of the SARS-CoV-2-outbreak: Simulation study about bias by incomplete case-detection
- PMID: 36288362
- PMCID: PMC9604981
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0276311
Epidemiological measures for assessing the dynamics of the SARS-CoV-2-outbreak: Simulation study about bias by incomplete case-detection
Abstract
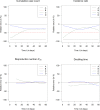
During the SARS-CoV-2 outbreak, several epidemiological measures, such as cumulative case-counts (CCC), incidence rates, effective reproduction numbers (Reff) and doubling times, have been used to inform the general public and to justify interventions such as lockdown. It has been very likely that not all infectious people have been identified during the course of the epidemic, which lead to incomplete case-detection. We compare CCC, incidence rates, Reff and doubling times in the presence of incomplete case-detection. For this, an infection-age-structured SIR model is used to simulate a SARS-CoV-2 outbreak followed by a lockdown in a hypothetical population. Different scenarios about temporal variations in case-detection are applied to the four measures during outbreak and lockdown. The biases resulting from incomplete case-detection on the four measures are compared in terms of relative errors. CCC is most prone to bias by incomplete case-detection in all of our settings. Reff is the least biased measure. The possibly biased CCC may lead to erroneous conclusions in cross-country comparisons. With a view to future reporting about this or other epidemics, we recommend including and placing an emphasis on Reff in those epidemiological measures used for informing the general public and policy makers.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have read the journal’s policy and have declared the following competing interests: TK received research grants from the Gemeinsamer Bundesausschuss (G-BA – Federal Joint Committee, Germany), the Bundesministerium für Gesundheit (BMG – Federal Ministry of Health, Germany) outside of the submitted work. He further has received personal compensation from Eli Lilly & Company, Teva Pharmaceuticals, Total Energies S.E., the BMJ, and Frontiers outside of the submitted work. This does not alter our adherence to PLOS ONE policies on sharing data and materials.
Figures



Similar articles
-
A cross-sectional national investigation of COVID-19 outbreaks in nurseries during rapid spread of the Alpha (B.1.1.7) variant of SARS-CoV-2 in England.BMC Public Health. 2022 Oct 2;22(1):1845. doi: 10.1186/s12889-022-14228-z. BMC Public Health. 2022. PMID: 36183069 Free PMC article.
-
Epidemic Landscape and Forecasting of SARS-CoV-2 in India.J Epidemiol Glob Health. 2021 Mar;11(1):55-59. doi: 10.2991/jegh.k.200823.001. Epub 2020 Aug 28. J Epidemiol Glob Health. 2021. PMID: 32959618 Free PMC article.
-
A modelling analysis of the effectiveness of second wave COVID-19 response strategies in Australia.Sci Rep. 2021 Jun 7;11(1):11958. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-91418-6. Sci Rep. 2021. PMID: 34099788 Free PMC article.
-
In the interest of public safety: rapid response to the COVID-19 epidemic in Vietnam.BMJ Glob Health. 2021 Jan;6(1):e004100. doi: 10.1136/bmjgh-2020-004100. BMJ Glob Health. 2021. PMID: 33495284 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Pandemic lockdown, healthcare policies and human rights: integrating opposed views on COVID-19 public health mitigation measures.Rev Cardiovasc Med. 2020 Dec 30;21(4):509-516. doi: 10.31083/j.rcm.2020.04.274. Rev Cardiovasc Med. 2020. PMID: 33387996 Review.
Cited by
-
Approximation of the infection-age-structured SIR model by the conventional SIR model of infectious disease epidemiology.Front Epidemiol. 2024 Dec 17;4:1429034. doi: 10.3389/fepid.2024.1429034. eCollection 2024. Front Epidemiol. 2024. PMID: 39741900 Free PMC article.
References
-
- German law for prevention and mitigation of infectious diseases §28a: Protective measures against the spread of the corona-virus disease-2019 (COVID-19) [Gesetz zur Verhütung und Bekämpfung von Infektionskrankheiten beim Menschen § 28a Besondere Schutzmaßnahmen zur Verhinderung der Verbreitung der Coronavirus-Krankheit-2019 (COVID-19)]
-
- Johns Hopkins University of Medicine, Coronavirus Resource Center (CRC) by the Center for Systems and Engineering (CSSE), https://coronavirus.jhu.edu/map.html, accessed on May 11th, 2021
-
- World Health Organization, Coronavirus disease (COVID-19) situation reports, https://www.who.int/emergencies/diseases/novel-coronavirus-2019/situatio..., accessed May 11th, 2021
-
- Merkel A. Transcript of press conference about the corona crisis. 2020 Apr 1 [Cited 2021 May 11]. Available from: https://www.bundesregierung.de/breg-de/suche/telefon-pressekonferenz-von...
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

