T Lymphocyte Serotonin 5-HT7 Receptor Is Dysregulated in Natalizumab-Treated Multiple Sclerosis Patients
- PMID: 36289679
- PMCID: PMC9599221
- DOI: 10.3390/biomedicines10102418
T Lymphocyte Serotonin 5-HT7 Receptor Is Dysregulated in Natalizumab-Treated Multiple Sclerosis Patients
Abstract
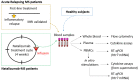
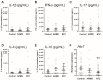
Serotonin (5-HT) is known as a potent immune cell modulator in autoimmune diseases and should be protective in the pathogenesis of multiple sclerosis (MS). Nevertheless, there is limited knowledge about receptors involved in 5-HT effects as well as induced mechanisms. Among 5-HT receptors, the 5-HT7 receptor is able to activate naïve T cells and influence the inflammatory response; however, its involvement in the disease has never been studied so far. In this study, we collected blood sample from three groups: acute relapsing MS patients (ARMS), natalizumab-treated MS patients (NTZ), and control subjects. We investigated the 5-HT7 expression on circulating lymphocytes and evaluated the effects of its activation on cytokine production with peripheral blood mononuclear cell (PBMC) cultures. We found a significant increase in the 5-HT7 surface expression on T lymphocytes and on the different CD4+ T cell subsets exclusively in NTZ-treated patients. We also showed that the selective agonist 5-carboxamidotryptamine (5-CT)-induced 5-HT7R activation significantly promotes the production of IL-10, a potent immunosuppressive cytokine in PBMCs. This study provides for the first time a dysregulation of 5-HT7 expression in NTZ-MS patients and its ability to promote IL-10 release, suggesting its protective role. These findings strengthen the evidence that 5-HT7 may play a role in the immuno-protective mechanisms of NTZ in MS disease and could be considered as an interesting therapeutic target in MS.
Keywords: 5-HT7 receptor; PBMCs (peripheral blood mononuclear cells); T lymphocyte (T-cell); interleukin-10 (IL-10); multiple sclerosis; natalizumab treatment; serotonin.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures


References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

