Multidrug-Resistant High-Risk Escherichia coli and Klebsiella pneumoniae Clonal Lineages Occur in Black-Headed Gulls from Two Conservation Islands in Germany
- PMID: 36290018
- PMCID: PMC9598702
- DOI: 10.3390/antibiotics11101357
Multidrug-Resistant High-Risk Escherichia coli and Klebsiella pneumoniae Clonal Lineages Occur in Black-Headed Gulls from Two Conservation Islands in Germany
Abstract
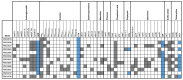
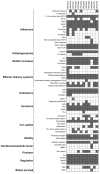
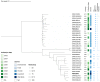
Multidrug-resistant (MDR) Enterobacterales, including extended-spectrum β-lactamase (ESBL)-producing Escherichia coli and Klebsiella pneumoniae, not only emerge in healthcare settings but also in other habitats, such as livestock and wildlife. The spread of these pathogens, which often combine resistance with high-level virulence, is a growing problem, as infections have become increasingly difficult to treat. Here, we investigated the occurrence of ESBL-producing E. coli and K. pneumoniae in fecal samples from two black-headed gull colonies breeding on two nature conservation islands in Western Pomerania, Germany. In addition to cloacal samples from adult birds (n = 211) and their nestlings (n = 99) during the 2021 breeding season, collective fecal samples (n = 29) were obtained. All samples were screened for ESBL producers, which were then subjected to whole-genome sequencing. We found a total of 12 ESBL-producing E. coli and K. pneumoniae consisting of 11 E. coli and 1 K. pneumoniae, and including the international high-risk E. coli sequence types (ST)131, ST38, and ST58. Eight of the investigated strains had a MDR genotype and carried a large repertoire of virulence-associated genes, including the pap operon, which is important for urinary tract infections. In addition, we identified many genes associated with adherence, biofilm formation, iron uptake, and toxin production. Finally, our analysis revealed the close phylogenetic relationship of ST38 strains with genomes originating from human sources, underlining their zoonotic and pathogenic character. This study highlights the importance of the One Health approach, and thus the interdependence between human and animal health and their surrounding environment.
Keywords: One Health; antimicrobial resistance; black-headed gulls; next-generation sequencing; virulence; wildlife.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Cross-border emergence of clonal lineages of ST38 Escherichia coli producing the OXA-48-like carbapenemase OXA-244 in Germany and Switzerland.Int J Antimicrob Agents. 2020 Dec;56(6):106157. doi: 10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2020.106157. Epub 2020 Sep 9. Int J Antimicrob Agents. 2020. PMID: 32919009
-
Clinically Relevant ESBL-Producing K. pneumoniae ST307 and E. coli ST38 in an Urban West African Rat Population.Front Microbiol. 2018 Feb 9;9:150. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2018.00150. eCollection 2018. Front Microbiol. 2018. PMID: 29479341 Free PMC article.
-
Changes in Fecal Carriage of Extended-Spectrum β-Lactamase Producing Enterobacterales in Dutch Veal Calves by Clonal Spread of Klebsiella pneumoniae.Front Microbiol. 2022 Jun 23;13:866674. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2022.866674. eCollection 2022. Front Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 35814663 Free PMC article.
-
Occurrence of the Colistin Resistance Gene mcr-1 and Additional Antibiotic Resistance Genes in ESBL/AmpC-Producing Escherichia coli from Poultry in Lebanon: A Nationwide Survey.Microbiol Spectr. 2021 Oct 31;9(2):e0002521. doi: 10.1128/Spectrum.00025-21. Epub 2021 Sep 8. Microbiol Spectr. 2021. PMID: 34494875 Free PMC article.
-
GENOMIC CHARACTERIZATION OF MULTIDRUG-RESISTANT EXTENDED-SPECTRUM β-LACTAMASE-PRODUCING ESCHERICHIA COLI AND KLEBSIELLA PNEUMONIAE FROM CHIMPANZEES (PAN TROGLODYTES) FROM WILD AND SANCTUARY LOCATIONS IN UGANDA.J Wildl Dis. 2022 Apr 1;58(2):269-278. doi: 10.7589/JWD-D-21-00068. J Wildl Dis. 2022. PMID: 35255126
Cited by
-
Prevalence and Virulence Profiles of Klebsiella pneumoniae Isolated From Different Animals.Vet Med Sci. 2025 Mar;11(2):e70243. doi: 10.1002/vms3.70243. Vet Med Sci. 2025. PMID: 39969166 Free PMC article.
-
Klebsiella in Wildlife: Clonal Dynamics and Antibiotic Resistance Profiles, a Systematic Review.Pathogens. 2024 Oct 30;13(11):945. doi: 10.3390/pathogens13110945. Pathogens. 2024. PMID: 39599498 Free PMC article.
-
Isolation of a CTX-M-55 (ESBL)-Producing Escherichia coli Strain of the Global ST6448 Clone from a Captive Orangutan in the USA.Curr Microbiol. 2024 May 17;81(7):177. doi: 10.1007/s00284-024-03693-x. Curr Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 38758473
-
Investigation of a Natural Antibiotic's Properties Effective against Resistant Opportunistic Pathogenic Infections.J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2025 Mar 19;35:e2409018. doi: 10.4014/jmb.2409.09018. J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2025. PMID: 40296839 Free PMC article.
-
Occurrence of ESBL- and AmpC-Producing E. coli in French Griffon Vultures Feeding on Extensive Livestock Carcasses.Antibiotics (Basel). 2023 Jul 7;12(7):1160. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics12071160. Antibiotics (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37508256 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Sherry N.L., Gorrie C.L., Kwong J.C., Higgs C., Stuart R.L., Marshall C., Ballard S.A., Sait M., Korman T.M., Slavin M.A., et al. Controlling Superbugs Study Group. Multi-site implementation of whole genome sequencing for hospital infection control: A prospective genomic epidemiological analysis. Lancet Reg. Health-West. Pac. 2022;23:100446. doi: 10.1016/j.lanwpc.2022.100446. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

