Genome-Wide Analysis of the Almond AP2/ERF Superfamily and Its Functional Prediction during Dormancy in Response to Freezing Stress
- PMID: 36290423
- PMCID: PMC9598233
- DOI: 10.3390/biology11101520
Genome-Wide Analysis of the Almond AP2/ERF Superfamily and Its Functional Prediction during Dormancy in Response to Freezing Stress
Abstract
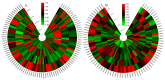
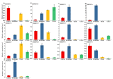
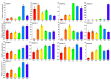
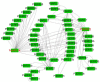
The AP2/ERF transcription factor family is one of the largest transcription factor families in plants and plays an important role in regulating plant growth and development and the response to biotic and abiotic stresses. However, there is no report on the AP2/ERF gene family in almond (Prunus dulcis). In this study, a total of 136 PdAP2/ERF genes were identified from the almond genome, and their protein physicochemical properties were analyzed. The PdAP2/ERF members were divided into five subgroups: AP2, RAV, ERF, DREB, and Soloist. The PdAP2/ERF members in each subgroup had conserved motif types and exon/intron numbers. PdAP2/ERFS members are distributed on eight chromosomes, with 22 pairs of segmental duplications and 28 pairs of tandem duplications. We further explored the colinear relationship between almond and Arabidopsis thaliana, Oryza sativa, Malus domestica, and Prunus persicaAP2/ERF genes and their evolution. The results of cis-acting elements showed that PdAP2/ERF members are widely involved in various processes, such as growth and development, hormone regulation, and stress response. The results based on transcriptome expression patterns showed that PdAP2/ERF genes had significant tissue-specific expression characteristics and were involved in the response of annual dormant branches of almond to low-temperature freezing stress. In addition, the fluorescence quantitative relative expression results of 13 representative PdAP2/ERF genes in four tissues of 'Wanfeng' almond and under six low-temperature freezing treatments of annual dormant branches were consistent with the transcriptome results. It is worth noting that the fluorescence quantitative expression level showed that the PdERF24 gene was extremely significant at -30 °C, suggesting that this gene may play an important role in the response of almond dormancy to ultralow temperature freezing stress. Finally, we identified 7424 and 6971 target genes based on AP2 and ERF/DREB DNA-binding sites, respectively. The GO and KEGG enrichment results showed that these target genes play important roles in protein function and multiple pathways. In summary, we conducted bioinformatics and expression pattern studies on PdAP2/ERF genes, including 13 PdAP2/ERF genes, and performed fluorescence quantitative analysis of annual dormant shoots under different low-temperature freezing stress treatments to understand the tolerance of almond dormancy to freezing stress and suggest future improvements.
Keywords: AP2/ERF gene family; Prunus dulcis; evolutionary analyses; expression patterns; freezing stress.
Conflict of interest statement
None of the authors have any competing interest to declare.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Genome-wide identification and comparative analysis of the AP2/ERF gene family in Prunus dulcis and Prunus tenella: expression of PdAP2/ERF genes under freezing stress during dormancy.BMC Genomics. 2025 Jan 31;26(1):95. doi: 10.1186/s12864-025-11275-9. BMC Genomics. 2025. PMID: 39891077 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-Wide Identification and Analysis of the MADS-Box Gene Family in Almond Reveal Its Expression Features in Different Flowering Periods.Genes (Basel). 2022 Sep 29;13(10):1764. doi: 10.3390/genes13101764. Genes (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36292648 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-wide identification and expression profiling analysis of maize AP2/ERF superfamily genes reveal essential roles in abiotic stress tolerance.BMC Genomics. 2022 Feb 12;23(1):125. doi: 10.1186/s12864-022-08345-7. BMC Genomics. 2022. PMID: 35151253 Free PMC article.
-
Understanding AP2/ERF Transcription Factor Responses and Tolerance to Various Abiotic Stresses in Plants: A Comprehensive Review.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Jan 11;25(2):893. doi: 10.3390/ijms25020893. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38255967 Free PMC article. Review.
-
AP2/ERF Transcription Factor Regulatory Networks in Hormone and Abiotic Stress Responses in Arabidopsis.Front Plant Sci. 2019 Feb 28;10:228. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2019.00228. eCollection 2019. Front Plant Sci. 2019. PMID: 30873200 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Genome-wide identification, structural characterization and expression profiling of AP2/ERF gene family in bayberry (Myrica rubra).BMC Plant Biol. 2024 Nov 28;24(1):1139. doi: 10.1186/s12870-024-05847-2. BMC Plant Biol. 2024. PMID: 39604860 Free PMC article.
-
Editorial to the Special Issue "Eco-Physiological and Molecular Basis of Stress Tolerance in Plants".Biology (Basel). 2023 Mar 22;12(3):485. doi: 10.3390/biology12030485. Biology (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36979176 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-wide analysis of the ABC gene family in almond and functional predictions during flower development, freezing stress, and salt stress.BMC Plant Biol. 2024 Jan 2;24(1):12. doi: 10.1186/s12870-023-04698-7. BMC Plant Biol. 2024. PMID: 38163883 Free PMC article.
-
Integrated metabolome and transcriptome analysis reveals potential mechanism during the bud dormancy transition of Astragalus membranaceus (Fisch.) Bge. var. mongholicus (Bge.) Hsiao.Front Plant Sci. 2025 Jan 21;15:1483538. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2024.1483538. eCollection 2024. Front Plant Sci. 2025. PMID: 39906223 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-wide identification and comparative analysis of the AP2/ERF gene family in Prunus dulcis and Prunus tenella: expression of PdAP2/ERF genes under freezing stress during dormancy.BMC Genomics. 2025 Jan 31;26(1):95. doi: 10.1186/s12864-025-11275-9. BMC Genomics. 2025. PMID: 39891077 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Liu J.-H., Peng T., Dai W. Critical cis-Acting Elements and Interacting Transcription Factors: Key Players Associated with Abiotic Stress Responses in Plants. Plant Mol. Biol. Rep. 2014;32:303–317. doi: 10.1007/s11105-013-0667-z. - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

