Quercetin Nanoemulsion Ameliorates Neuronal Dysfunction in Experimental Alzheimer's Disease Model
- PMID: 36290710
- PMCID: PMC9598210
- DOI: 10.3390/antiox11101986
Quercetin Nanoemulsion Ameliorates Neuronal Dysfunction in Experimental Alzheimer's Disease Model
Abstract
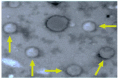
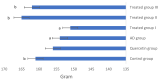
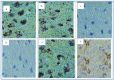
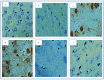
Aluminum is the most abundant metal that can get admission to the human through several means that include our food, drinking water, cans, drugs, and deodorants, causing neurodegenerative diseases such as Alzheimer's disease (AD). The present study aims to evaluate the role of quercetin nanoemulsion (QCNE) in attenuating neuronal dysfunction in aluminum chloride (AlCl3)-induced experimental AD. All animals were classified into six groups including negative control group (I): received a vehicle; QC group: received intraperitoneal (IP) injection of QC; Alzheimer's group: received AlCl3 orally; treated group (I): received AlCl3 orally and IP injection of QC; treated group (II): received AlCl3 orally and QC orally; and treated group (III): received AlCl3 orally and IP injection of QCNE. At the end of the experimental period (30 days), the brain was used to study biochemical parameters (measurement of neurotransmitters (serotonin, dopamine, and norepinephrine), oxidant/antioxidant parameters (reduced glutathione, malondialdehyde, superoxide dismutase, and advanced oxidation protein product), and inflammatory markers (adiponectin, interleukin 1β, and plasma tumor necrosis factor-alpha)), while another part was for brain immune-histochemical analysis (study cyclooxygenases (COX-1 and COX-2)). Results showed that the mean value of oxidative stress markers was significantly increased in the AD group as well as the inflammatory biomarkers and all the study neurotransmitters, whereas these parameters were attenuated in treated groups, especially those that received QCNE. The immunohistochemistry findings confirm our results. Both approaches (QC and QCNE) succeeded in retracting the negative impact of AlCl3. Meanwhile, the effect of QCNE is more potent in mitigating the impact mediated by AlCl3 in treated animals. In conclusion, the treatment mainly by QCNE has huge potential in protecting against AlCl3-induced neuronal dysfunction, as shown in our results by the elevation of brain antioxidant/anti-inflammatory activities and neurotransmitter levels as well as mending of the histopathological changes in animal models.
Keywords: Alzheimer’s disease; immunohistochemistry; nanoemulsion; oxidative; quercetin; rats.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Prema A., Thenmozhi A.J., Manivasagam T., Essa M.M., Akbar M.D., Akbar M. Fenugreek Seed Powder Nullified Aluminium Chloride Induced Memory Loss, Biochemical Changes, Aβ Burden and Apoptosis via Regulating Akt/GSK3β Signaling Pathway. PLoS ONE. 2016;11:e01659552016. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0165955. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

