Rationale Efficacy and Safety Evidence of Lenvatinib and Pembrolizumab Association in Anaplastic Thyroid Carcinoma
- PMID: 36290887
- PMCID: PMC9601195
- DOI: 10.3390/curroncol29100610
Rationale Efficacy and Safety Evidence of Lenvatinib and Pembrolizumab Association in Anaplastic Thyroid Carcinoma
Abstract
Anaplastic thyroid carcinoma (ATC) are highly aggressive malignant tumors with poor overall prognosis despite multimodal therapy. As ATC are extremely rare, no randomized controlled study has been published for metastatic disease. Thyrosine kinase inhibitors, especially lenvatinib and immune checkpoint inhibitors such as pembrolizumab, are emerging drugs for ATC. Few studies have reported the efficacity of pembrolizumab and lenvatinib association, resulting in its frequent off-label use. In this review, we discuss rationale efficacy and safety evidence for the association of lenvatinib and pembrolizumab in ATC. First, we discuss preclinical rationale for pembrolizumab monotherapy, lenvatinib monotherapy and synergistic action of pembrolizumab and lenvatinib in the metastatic setting. We also discuss clinical evidence for immunotherapy and pembrolizumab in ATC through the analysis of studies evaluating immunotherapy, lenvatinib and pembrolizumab lenvatinib association in ATC. In addition, we discuss the safety of this association and potential predictive biomarkers of efficiency.
Keywords: anaplastic thyroid cell carcinoma; lenvatinib; pembrolizumab; rationale; treatment.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
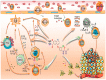
References
-
- Cancer Statistics Review, 1975–2013—Previous Version—SEER Cancer Statistics Review. [(accessed on 1 September 2022)]; Available online: https://seer.cancer.gov/archive/csr/1975_2013/index.html.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

