mRNA-Based Approaches to Treating Liver Diseases
- PMID: 36291194
- PMCID: PMC9601253
- DOI: 10.3390/cells11203328
mRNA-Based Approaches to Treating Liver Diseases
Abstract
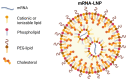
Diseases that affect the liver account for approximately 2 million deaths worldwide each year. The increasing prevalence of these diseases and the limited efficacy of current treatments are expected to stimulate substantial growth in the global market for therapeutics that target the liver. Currently, liver transplantation is the only curative option available for many liver diseases. Gene therapy represents a valuable approach to treatment. The liver plays a central role in a myriad of essential metabolic functions, making it an attractive organ for gene therapy; hepatocytes comprise the most relevant target. To date, viral vectors constitute the preferred approach to targeting hepatocytes with genes of therapeutic interest. Alternatively, mRNA-based therapy offers a number of comparative advantages. Clinical and preclinical studies undertaken to treat inherited metabolic diseases affecting the liver, cirrhosis and fibrosis, hepatocellular carcinoma, hepatitis B, and cytomegalovirus using lipid nanoparticle-encapsulated mRNAs that encode the therapeutic or antigenic protein of interest are discussed.
Keywords: cirrhosis; hepatocellular carcinoma; inherited metabolic diseases; lipid nanoparticles; therapeutic mRNA constructs.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Advances in nanoparticle-based mRNA delivery for liver cancer and liver-associated infectious diseases.Nanoscale Horiz. 2022 Dec 20;8(1):10-28. doi: 10.1039/d2nh00289b. Nanoscale Horiz. 2022. PMID: 36260016 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Therapeutic HNF4A mRNA attenuates liver fibrosis in a preclinical model.J Hepatol. 2021 Dec;75(6):1420-1433. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2021.08.011. Epub 2021 Aug 25. J Hepatol. 2021. PMID: 34453962
-
A Single Dose of Anti-HBsAg Antibody-Encoding mRNA-LNPs Suppressed HBsAg Expression: a Potential Cure of Chronic Hepatitis B Virus Infection.mBio. 2022 Aug 30;13(4):e0161222. doi: 10.1128/mbio.01612-22. Epub 2022 Jul 7. mBio. 2022. PMID: 35862767 Free PMC article.
-
Lipid-based nanoparticle technologies for liver targeting.Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2020;154-155:79-101. doi: 10.1016/j.addr.2020.06.017. Epub 2020 Jun 20. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2020. PMID: 32574575 Review.
-
Lipid Nanoparticle Systems for Enabling Gene Therapies.Mol Ther. 2017 Jul 5;25(7):1467-1475. doi: 10.1016/j.ymthe.2017.03.013. Epub 2017 Apr 13. Mol Ther. 2017. PMID: 28412170 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Lipid nanoparticle-based mRNA delivery systems for cancer immunotherapy.Nano Converg. 2023 Aug 7;10(1):36. doi: 10.1186/s40580-023-00385-3. Nano Converg. 2023. PMID: 37550567 Free PMC article. Review.
-
High-density brush-shaped polymer lipids reduce anti-PEG antibody binding for repeated administration of mRNA therapeutics.Nat Mater. 2025 Feb 28. doi: 10.1038/s41563-024-02116-3. Online ahead of print. Nat Mater. 2025. PMID: 40021827
-
mRNA-LNP vaccine strategies: Effects of adjuvants on non-parenchymal liver cells and tolerance.Mol Ther Methods Clin Dev. 2025 Feb 4;33(1):101427. doi: 10.1016/j.omtm.2025.101427. eCollection 2025 Mar 13. Mol Ther Methods Clin Dev. 2025. PMID: 40027262 Free PMC article.
-
Enhancing Cytoplasmic Expression of Exogenous mRNA Through Dynamic Mechanical Stimulation.Adv Healthc Mater. 2025 Jan;14(1):e2401918. doi: 10.1002/adhm.202401918. Epub 2024 Oct 23. Adv Healthc Mater. 2025. PMID: 39440644
-
Deciphering hepatocellular carcinoma pathogenesis and therapeutics: a study on anoikis, ceRNA regulatory network and traditional Chinese medicine.Front Pharmacol. 2024 Jan 12;14:1325992. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2023.1325992. eCollection 2023. Front Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 38283837 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

