Profiles of Caregiver-Reported Executive Function in Children with Down Syndrome
- PMID: 36291267
- PMCID: PMC9599143
- DOI: 10.3390/brainsci12101333
Profiles of Caregiver-Reported Executive Function in Children with Down Syndrome
Abstract
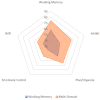
Children with Down syndrome (DS) are at risk for challenges with aspects of executive function (EF). The current study explores whether heterogeneity in EF profiles can be detected within a sample of children with DS. Participants were 69 children with DS, ages 3-10 years (M = 6.23, SD = 1.91). T-scores from a caregiver-report measure of executive function were modeled using latent profile analysis, and auxiliary analyses examined the association between demographic and biomedical factors and probability of profile membership. The two-profile solution was the best fit for the sample, with a profile that involved elevated scores in working memory only ("Working Memory Only" profile; 43% of sample) and a "Multi-Domain" profile that involved elevated scores in planning, inhibition, and working memory (57%). The presence of congenital heart defects was associated with a higher probability of assignment to the Multi-Domain profile. Findings from this study contribute to the characterization of heterogeneous outcomes associated with DS.
Keywords: Down syndrome; executive function; latent profile analysis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures
References
-
- Laureys F., De Waelle S., Barendse M.T., Lenoir M., Deconinck F.J. The factor structure of executive function in childhood and adolescence. Intelligence. 2022;90:101600. doi: 10.1016/j.intell.2021.101600. - DOI
-
- Hendry A., Jones E.J., Charman T. Executive function in the first three years of life: Precursors, predictors and patterns. Dev. Rev. 2016;42:1–33. doi: 10.1016/j.dr.2016.06.005. - DOI