Assessment of Lipid Quality in Commercial Omega-3 Supplements Sold in the French Market
- PMID: 36291569
- PMCID: PMC9599935
- DOI: 10.3390/biom12101361
Assessment of Lipid Quality in Commercial Omega-3 Supplements Sold in the French Market
Abstract
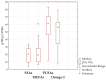
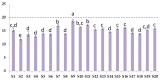
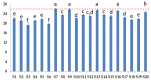
Supplementation of omega-3 fatty acids is considered a valuable strategy to supply the low intake of these fatty acids. Thus, the safety of the supplements is an important milestone. Because of that, we analyzed 20 unflavored supplements sold in the French market for fatty acid and triglyceride composition, for EPA and DHA, and for tocol content, as well as for oxidative status. This study found that only 2.5% of the supplements did not meet their label claims for omega-3 content. TAG analysis showed high variability among the triglyceride distribution, and the same trend was also noticed for the tocol content; in fact, a high variability of the distribution of the six tocols (four tocopherols and two tocotrienols) was found among the samples. Of the tested products, all of them complied with peroxide value, p-anisidine value, and Totox values established by the Global Organization for EPA and DHA Omega-3s (GOED) and were not oxidized.
Keywords: Schizochytrium; Totox; fish oil; lipid oxidation; microalgae oil; p-anisidine value; peroxide value; polyunsaturated fatty acids.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures





References
-
- Giacobbe J., Benoiton B., Zunszain P., Pariante C.M., Borsini A. The Anti-Inflammatory Role of Omega-3 Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids Metabolites in Pre-Clinical Models of Psychiatric, Neurodegenerative, and Neurological Disorders. Front. Psychiatry. 2020;11:122. doi: 10.3389/fpsyt.2020.00122. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Román G.C., Jackson R.E., Gadhia R., Román A.N., Reis J. Mediterranean diet: The role of long-chain v-3 fatty acids in fish; polyphenols in fruits, vegetables, cereals, coffee, tea, cacao and wine; probiotics and vitamins in prevention of stroke, age-related cognitive decline, and Alzheimer disease. Rev. Neurol. 2019;175:724–741. doi: 10.1016/j.neurol.2019.08.005. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

