A Synergistic Effect between Plasma Dickkopf-1 and Obstructive Coronary Artery Disease on the Prediction of Major Adverse Cardiac Events in Patients with Angina: An Observational Study
- PMID: 36291617
- PMCID: PMC9599804
- DOI: 10.3390/biom12101408
A Synergistic Effect between Plasma Dickkopf-1 and Obstructive Coronary Artery Disease on the Prediction of Major Adverse Cardiac Events in Patients with Angina: An Observational Study
Abstract
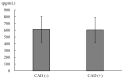
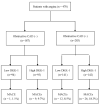
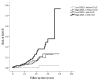
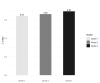
The canonical β-catenin-dependent wingless (Wnt) pathway is associated with endothelial function. We examined the effect of plasma dickkopf-1 (DKK-1), an inhibitor of the Wnt pathway, on the prediction of major adverse cardiac events (MACEs). We enrolled patients who had undergone selective coronary angiography for angina. DKK-1 levels were determined using plasma collected at the outpatient visit after fasting. MACEs served as the primary endpoint. All 470 enrolled patients were divided into four groups according to their median plasma DKK-1 levels and the presence of obstructive coronary artery disease (CAD). Forty-eight patients reached the primary endpoint during a median follow-up time of 4.8 years. Kaplan-Meier survival analysis indicated that the group with high DKK-1 and obstructive CAD had a significantly higher mortality rate than the other three groups (log-rank test p = 0.001). Compared with the low plasma DKK-1 without significant coronary obstruction group, the high DKK-1 with obstructive CAD group had a hazard ratio of 10.640 (95% confidence interval: 1.350-83.874) for MACEs, as determined by multivariable Cox proportional hazard regression analysis. In conclusion, we observed a synergistic effect between high plasma DKK-1 and obstructive CAD on the prediction of MACEs in patients with angina.
Keywords: coronary artery disease; death; dickkopf-1; major adverse cardiac events; myocardial infarction; obstruction; stroke.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Prognostic value of coronary computed tomography angiography in stroke patients.Atherosclerosis. 2015 Feb;238(2):271-7. doi: 10.1016/j.atherosclerosis.2014.10.102. Epub 2014 Nov 4. Atherosclerosis. 2015. PMID: 25544177
-
Influence of symptom typicality for predicting MACE in patients without obstructive coronary artery disease: From the CONFIRM Registry (Coronary Computed Tomography Angiography Evaluation for Clinical Outcomes: An International Multicenter Registry).Clin Cardiol. 2018 May;41(5):586-593. doi: 10.1002/clc.22940. Epub 2018 May 11. Clin Cardiol. 2018. PMID: 29521447 Free PMC article.
-
Elevated plasma angiotensin converting enzyme 2 activity is an independent predictor of major adverse cardiac events in patients with obstructive coronary artery disease.PLoS One. 2018 Jun 13;13(6):e0198144. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0198144. eCollection 2018. PLoS One. 2018. PMID: 29897923 Free PMC article.
-
Age-related risk of major adverse cardiac event risk and coronary artery disease extent and severity by coronary CT angiography: results from 15 187 patients from the International Multisite CONFIRM Study.Eur Heart J Cardiovasc Imaging. 2014 May;15(5):586-94. doi: 10.1093/ehjci/jet132. Eur Heart J Cardiovasc Imaging. 2014. PMID: 24714312 Free PMC article.
-
Long-term prognostic value of whole-heart coronary magnetic resonance angiography.J Cardiovasc Magn Reson. 2021 May 17;23(1):56. doi: 10.1186/s12968-021-00749-w. J Cardiovasc Magn Reson. 2021. PMID: 33993891 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Plasma Dickkopf-1 Levels Are Associated with Chronic Kidney Disease.Metabolites. 2025 Apr 30;15(5):300. doi: 10.3390/metabo15050300. Metabolites. 2025. PMID: 40422877 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Khan M.A., Hashim M.J., Mustafa H., Baniyas M.Y., Al Suwaidi S., AlKatheeri R., Alblooshi F.M.K., Almatrooshi M., Alzaabi M.E.H., Al Darmaki R.S., et al. Global Epidemiology of Ischemic Heart Disease: Results from the Global Burden of Disease Study. Cureus. 2020;12:e9349. doi: 10.7759/cureus.9349. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Dai H., Much A.A., Maor E., Asher E., Younis A., Xu Y., Lu Y., Liu X., Shu J., Bragazzi N.L. Global, regional, and national burden of ischemic heart disease and its attributable risk factors, 1990–2017: Results from the global Burden of Disease Study 2017. Eur. Heart J. Qual. Care Clin. Outcomes. 2022;8:50–60. doi: 10.1093/ehjqcco/qcaa076. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- GBD 2017 Causes of Death Collaborators Global, regional, and national age-sex-specific mortality for 282 causes of death in 195 countries and territories, 1980–2017: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2017. Lancet. 2018;392:1736–1788. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(18)32203-7. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

