Nusinersen Induces Disease-Severity-Specific Neurometabolic Effects in Spinal Muscular Atrophy
- PMID: 36291640
- PMCID: PMC9599672
- DOI: 10.3390/biom12101431
Nusinersen Induces Disease-Severity-Specific Neurometabolic Effects in Spinal Muscular Atrophy
Abstract
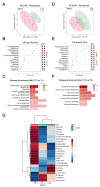
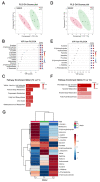
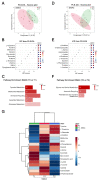
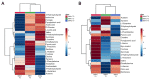
Intrathecal delivery of Nusinersen-an antisense oligonucleotide that promotes survival motor neuron (SMN) protein induction-is an approved therapy for spinal muscular atrophy (SMA). Here, we employed nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectroscopy to longitudinally characterize the unknown metabolic effects of Nusinersen in the cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) of SMA patients across disease severity. Modulation of amino acid metabolism is a common denominator of biochemical changes induced by Nusinersen, with distinct downstream metabolic effects according to disease severity. In severe SMA1 patients, Nusinersen stimulates energy-related glucose metabolism. In intermediate SMA2 patients, Nusinersen effects are also related to energy homeostasis but involve ketone body and fatty acid biosynthesis. In milder SMA3 patients, Nusinersen mainly modulates amino acid metabolism. Moreover, Nusinersen modifies the CSF metabolome of a more severe clinical group towards the profile of untreated SMA patients with milder disease. These findings reveal disease severity-specific neurometabolic signatures of Nusinersen treatment, suggesting a selective modulation of peripheral organ metabolism by this CNS-directed therapy in severe SMA patients.
Keywords: cerebrospinal fluid (CSF); nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR); nusinersen; spinal muscular atrophy (SMA); survival motor neuron (SMN).
Conflict of interest statement
C.B. received advisory board honoraria from Avexis, Biogen, Novartis, and Roche. The other authors declare that no conflict of interest exist.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Proteomics profiling and machine learning in nusinersen-treated patients with spinal muscular atrophy.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2024 Sep 10;81(1):393. doi: 10.1007/s00018-024-05426-6. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2024. PMID: 39254732 Free PMC article.
-
Treatment of Symptomatic Spinal Muscular Atrophy with Nusinersen: A Prospective Longitudinal Study on Scoliosis Progression.J Neuromuscul Dis. 2024;11(2):349-359. doi: 10.3233/JND-230077. J Neuromuscul Dis. 2024. PMID: 38363614 Free PMC article.
-
Nusinersen: A Review in 5q Spinal Muscular Atrophy.CNS Drugs. 2021 Dec;35(12):1317-1328. doi: 10.1007/s40263-021-00878-x. Epub 2021 Nov 30. CNS Drugs. 2021. PMID: 34850360 Free PMC article.
-
Nusinersen: First Global Approval.Drugs. 2017 Mar;77(4):473-479. doi: 10.1007/s40265-017-0711-7. Drugs. 2017. PMID: 28229309 Review.
-
Nusinersen: A Treatment for Spinal Muscular Atrophy.Ann Pharmacother. 2019 Jan;53(1):61-69. doi: 10.1177/1060028018789956. Epub 2018 Jul 16. Ann Pharmacother. 2019. PMID: 30008228 Review.
Cited by
-
SMN deficiency perturbs monoamine neurotransmitter metabolism in spinal muscular atrophy.Commun Biol. 2023 Nov 13;6(1):1155. doi: 10.1038/s42003-023-05543-1. Commun Biol. 2023. PMID: 37957344 Free PMC article.
-
Multi-omics profiling of CSF from spinal muscular atrophy type 3 patients after nusinersen treatment: a 2-year follow-up multicenter retrospective study.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2023 Aug 5;80(8):241. doi: 10.1007/s00018-023-04885-7. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2023. PMID: 37543540 Free PMC article.
-
Measuring Fatigue and Fatigability in Spinal Muscular Atrophy (SMA): Challenges and Opportunities.J Clin Med. 2023 May 14;12(10):3458. doi: 10.3390/jcm12103458. J Clin Med. 2023. PMID: 37240564 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Dysregulated balance of D- and L-amino acids modulating glutamatergic neurotransmission in severe spinal muscular atrophy.Neurobiol Dis. 2025 Apr;207:106849. doi: 10.1016/j.nbd.2025.106849. Epub 2025 Feb 24. Neurobiol Dis. 2025. PMID: 40010612 Free PMC article.
-
Dysregulation of cerebrospinal fluid metabolism profiles in spinal muscular atrophy patients: a case control study.Ital J Pediatr. 2024 Aug 22;50(1):154. doi: 10.1186/s13052-024-01726-6. Ital J Pediatr. 2024. PMID: 39175089 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Naryshkin N.A., Weetall M., Dakka A., Narasimhan J., Zhao X., Feng Z., Ling K.K., Karp G.M., Qi H., Woll M.G., et al. Motor neuron disease. SMN2 splicing modifiers improve motor function and longevity in mice with spinal muscular atrophy. Science. 2014;345:688–693. doi: 10.1126/science.1250127. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

