Nusinersen Induces Disease-Severity-Specific Neurometabolic Effects in Spinal Muscular Atrophy
- PMID: 36291640
- PMCID: PMC9599672
- DOI: 10.3390/biom12101431
Nusinersen Induces Disease-Severity-Specific Neurometabolic Effects in Spinal Muscular Atrophy
Abstract
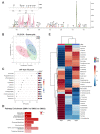
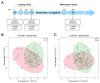
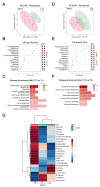
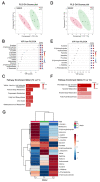
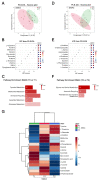
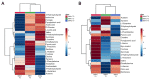
Intrathecal delivery of Nusinersen-an antisense oligonucleotide that promotes survival motor neuron (SMN) protein induction-is an approved therapy for spinal muscular atrophy (SMA). Here, we employed nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectroscopy to longitudinally characterize the unknown metabolic effects of Nusinersen in the cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) of SMA patients across disease severity. Modulation of amino acid metabolism is a common denominator of biochemical changes induced by Nusinersen, with distinct downstream metabolic effects according to disease severity. In severe SMA1 patients, Nusinersen stimulates energy-related glucose metabolism. In intermediate SMA2 patients, Nusinersen effects are also related to energy homeostasis but involve ketone body and fatty acid biosynthesis. In milder SMA3 patients, Nusinersen mainly modulates amino acid metabolism. Moreover, Nusinersen modifies the CSF metabolome of a more severe clinical group towards the profile of untreated SMA patients with milder disease. These findings reveal disease severity-specific neurometabolic signatures of Nusinersen treatment, suggesting a selective modulation of peripheral organ metabolism by this CNS-directed therapy in severe SMA patients.
Keywords: cerebrospinal fluid (CSF); nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR); nusinersen; spinal muscular atrophy (SMA); survival motor neuron (SMN).
Conflict of interest statement
C.B. received advisory board honoraria from Avexis, Biogen, Novartis, and Roche. The other authors declare that no conflict of interest exist.
Figures
References
-
- Naryshkin N.A., Weetall M., Dakka A., Narasimhan J., Zhao X., Feng Z., Ling K.K., Karp G.M., Qi H., Woll M.G., et al. Motor neuron disease. SMN2 splicing modifiers improve motor function and longevity in mice with spinal muscular atrophy. Science. 2014;345:688–693. doi: 10.1126/science.1250127. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

