Looking at the Pathogenesis of the Rabies Lyssavirus Strain Pasteur Vaccins through a Prism of the Disorder-Based Bioinformatics
- PMID: 36291645
- PMCID: PMC9599798
- DOI: 10.3390/biom12101436
Looking at the Pathogenesis of the Rabies Lyssavirus Strain Pasteur Vaccins through a Prism of the Disorder-Based Bioinformatics
Abstract
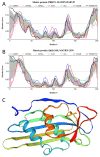
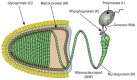
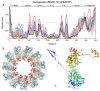
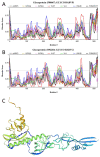
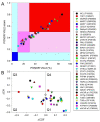
Rabies is a neurological disease that causes between 40,000 and 70,000 deaths every year. Once a rabies patient has become symptomatic, there is no effective treatment for the illness, and in unvaccinated individuals, the case-fatality rate of rabies is close to 100%. French scientists Louis Pasteur and Émile Roux developed the first vaccine for rabies in 1885. If administered before the virus reaches the brain, the modern rabies vaccine imparts long-lasting immunity to the virus and saves more than 250,000 people every year. However, the rabies virus can suppress the host's immune response once it has entered the cells of the brain, making death likely. This study aimed to make use of disorder-based proteomics and bioinformatics to determine the potential impact that intrinsically disordered protein regions (IDPRs) in the proteome of the rabies virus might have on the infectivity and lethality of the disease. This study used the proteome of the Rabies lyssavirus (RABV) strain Pasteur Vaccins (PV), one of the best-understood strains due to its use in the first rabies vaccine, as a model. The data reported in this study are in line with the hypothesis that high levels of intrinsic disorder in the phosphoprotein (P-protein) and nucleoprotein (N-protein) allow them to participate in the creation of Negri bodies and might help this virus to suppress the antiviral immune response in the host cells. Additionally, the study suggests that there could be a link between disorder in the matrix (M) protein and the modulation of viral transcription. The disordered regions in the M-protein might have a possible role in initiating viral budding within the cell. Furthermore, we checked the prevalence of functional disorder in a set of 37 host proteins directly involved in the interaction with the RABV proteins. The hope is that these new insights will aid in the development of treatments for rabies that are effective after infection.
Keywords: intrinsic disorder; intrinsically disordered protein; intrinsically disordered protein region; protein–protein interaction; rabies.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Rupprecht C.E. Rhabdoviruses: Rabies Virus. In: Baron S., editor. Medical Microbiology. 4th ed. University of Texas Medical Branch; Galveston, TX, USA: 1996. - PubMed
-
- ViralZone. Lyssavirus. [(accessed on 20 July 2020)]. Available online: https://viralzone.expasy.org/resources/Rhabdoviridae_virion.jpg.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

