Inhibition of Phosphoglycerate Dehydrogenase Radiosensitizes Human Colorectal Cancer Cells under Hypoxic Conditions
- PMID: 36291844
- PMCID: PMC9599856
- DOI: 10.3390/cancers14205060
Inhibition of Phosphoglycerate Dehydrogenase Radiosensitizes Human Colorectal Cancer Cells under Hypoxic Conditions
Abstract
Augmented de novo serine synthesis activity is increasingly apparent in distinct types of cancers and has mainly sparked interest by investigation of phosphoglycerate dehydrogenase (PHGDH). Overexpression of PHGDH has been associated with higher tumor grade, shorter relapse time and decreased overall survival. It is well known that therapeutic outcomes in cancer patients can be improved by reprogramming metabolic pathways in combination with standard treatment options, for example, radiotherapy. In this study, possible metabolic changes related to radioresponse were explored upon PHGDH inhibition. Additionally, we evaluated whether PHGDH inhibition could improve radioresponse in human colorectal cancer cell lines in both aerobic and radiobiological relevant hypoxic conditions. Dysregulation of reactive oxygen species (ROS) homeostasis and dysfunction in mitochondrial energy metabolism and oxygen consumption rate were indicative of potential radiomodulatory effects. We demonstrated that PHGDH inhibition radiosensitized hypoxic human colorectal cancer cells while leaving intrinsic radiosensitivity unaffected. In a xenograft model, the first hints of additive effects between PHGDH inhibition and radiotherapy were demonstrated. In conclusion, this study is the first to show that modulation of de novo serine biosynthesis enhances radioresponse in hypoxic colorectal cancer cells, mainly mediated by increased levels of intracellular ROS.
Keywords: colorectal cancer; hypoxia; radiosensitivity; reactive oxygen species; serine synthesis pathway.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



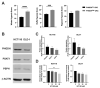
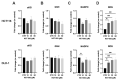

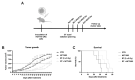
Similar articles
-
Overcoming erlotinib resistance in EGFR mutation-positive lung adenocarcinomas through repression of phosphoglycerate dehydrogenase.Theranostics. 2018 Feb 12;8(7):1808-1823. doi: 10.7150/thno.23177. eCollection 2018. Theranostics. 2018. PMID: 29556358 Free PMC article.
-
Dichloroacetate Radiosensitizes Hypoxic Breast Cancer Cells.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Dec 9;21(24):9367. doi: 10.3390/ijms21249367. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 33316932 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibition of 3-phosphoglycerate dehydrogenase (PHGDH) by indole amides abrogates de novo serine synthesis in cancer cells.Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2019 Sep 1;29(17):2503-2510. doi: 10.1016/j.bmcl.2019.07.011. Epub 2019 Jul 6. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2019. PMID: 31327531 Free PMC article.
-
3-Phosphoglycerate dehydrogenase: a potential target for cancer treatment.Cell Oncol (Dordr). 2021 Jun;44(3):541-556. doi: 10.1007/s13402-021-00599-9. Epub 2021 Mar 18. Cell Oncol (Dordr). 2021. PMID: 33735398 Review.
-
Can small molecular inhibitors that stop de novo serine synthesis be used in cancer treatment?Cell Death Discov. 2021 Apr 30;7(1):87. doi: 10.1038/s41420-021-00474-4. Cell Death Discov. 2021. PMID: 33931592 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Understanding the molecular mechanism responsible for developing therapeutic radiation-induced radioresistance of rectal cancer and improving the clinical outcomes of radiotherapy - A review.Cancer Biol Ther. 2024 Dec 31;25(1):2317999. doi: 10.1080/15384047.2024.2317999. Epub 2024 Mar 6. Cancer Biol Ther. 2024. PMID: 38445632 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Repurposing Sulfasalazine as a Radiosensitizer in Hypoxic Human Colorectal Cancer.Cancers (Basel). 2023 Apr 18;15(8):2363. doi: 10.3390/cancers15082363. Cancers (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37190291 Free PMC article.
-
Serine Metabolic Reprogramming in Tumorigenesis, Tumor Immunity, and Clinical Treatment.Adv Nutr. 2023 Sep;14(5):1050-1066. doi: 10.1016/j.advnut.2023.05.007. Epub 2023 May 13. Adv Nutr. 2023. PMID: 37187454 Free PMC article. Review.
-
PHGDH: a novel therapeutic target in cancer.Exp Mol Med. 2024 Jul;56(7):1513-1522. doi: 10.1038/s12276-024-01268-1. Epub 2024 Jul 1. Exp Mol Med. 2024. PMID: 38945960 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Sullivan M.R., Mattaini K.R., Dennstedt E.A., Nguyen A.A., Sivanand S., Reilly M.F., Meeth K., Muir A., Darnell A.M., Bosenberg M.W., et al. Increased Serine Synthesis Provides an Advantage for Tumors Arising in Tissues Where Serine Levels Are Limiting. Cell Metab. 2019;29:1410–1421.e4. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2019.02.015. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

