Impact of T790M Mutation Status on Later-Line Osimertinib Treatment in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Patients
- PMID: 36291877
- PMCID: PMC9600420
- DOI: 10.3390/cancers14205095
Impact of T790M Mutation Status on Later-Line Osimertinib Treatment in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Patients
Abstract
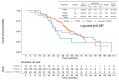
Background: Osimertinib is a third-generation epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitor (EGFR-TKI) designed to overcome acquired T790M resistance mutations in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). However, the efficacy of osimertinib in patients without acquired T790M mutations has not been well studied. This study aimed to evaluate the efficacy of osimertinib in patients treated with first- and second-generation EGFR-TKIs followed by later-line osimertinib treatment. Patients: The clinical data and survival outcomes of 172 patients with advanced NSCLC treated with osimertinib following frontline EGFR-TKIs at Chang Gung Memorial Hospital from 2014 to 2018 were retrospectively reviewed. T790M mutations were detected using tissue sequencing and/or liquid biopsy. Results: A total of 172 EGFR-mutated NSCLC patients treated with frontline EGFR-TKI therapy followed by later-line osimertinib were enrolled in the current study and divided into three groups based on the T790M status (positive, negative, or unknown T790M). Patients with NSCLC harboring acquired T790M mutation treated with osimertinib had the best objective response rate (ORR) (52.6%, 25.0%, and 32.0%, p = 0.044), disease control rate (DCR) (79.3%, 41.7%, and 68.0%, p = 0.011), and progression-free survival (PFS, median PFS, 12.6, 3.1, 10.4 months, p = 0.001) among the three groups (positive, negative, and unknown T790M, respectively). However, a marked difference was found between positive and negative T790M mutations but not between positive and unknown T790M mutations. Univariate analysis was performed to identify potential prognostic factors for PFS in 172 patients treated with osimertinib. Lung metastasis (p < 0.001), brain metastasis (p < 0.009), number of metastatic sites (p < 0.001), PFS with frontline EGFR-TKIs (p = 0.03), and T790M status (p = 0.006) were identified as prognostic factors for PFS with osimertinib. Multivariate analysis showed that lung metastasis (p < 0.001) and PFS with frontline EGFR-TKIs and T790M status were independent prognostic factors. Conclusion: This study confirmed the greater efficacy of later-line osimertinib for NSCLC with acquired T790M mutation than for NSCLC without acquired T790M mutation. Detection of the T790M mutation after frontline treatment (first- and second-generation EGFR-TKI) is crucial for prolonging the survival of NSCLC patients harboring EGFR mutation. Osimertinib may be considered an option for NSCLC with unknown T790M mutations, as a certain subpopulation may benefit from osimertinib.
Keywords: T790M mutation; epidermal growth factor receptor; lung cancer; osimertinib.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Sequential treatment in advanced non-small cell lung cancer harboring EGFR mutations.Ther Adv Respir Dis. 2022 Jan-Dec;16:17534666221132731. doi: 10.1177/17534666221132731. Ther Adv Respir Dis. 2022. PMID: 36305280 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of the generation of EGFR-TKIs administered as prior therapy on the efficacy of osimertinib in patients with non-small cell lung cancer harboring EGFR T790M mutation.Thorac Cancer. 2021 Feb;12(3):329-338. doi: 10.1111/1759-7714.13742. Epub 2020 Nov 21. Thorac Cancer. 2021. PMID: 33219754 Free PMC article.
-
Osimertinib, a third-generation EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitor: A retrospective multicenter study of its real-world efficacy and safety in advanced/recurrent non-small cell lung carcinoma.Thorac Cancer. 2020 Apr;11(4):935-942. doi: 10.1111/1759-7714.13378. Epub 2020 Mar 4. Thorac Cancer. 2020. PMID: 32129931 Free PMC article.
-
Efficacy of Osimertinib in EGFR-Mutated Advanced Non-small-Cell Lung Cancer With Different T790M Status Following Resistance to Prior EGFR-TKIs: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis.Front Oncol. 2022 Jun 7;12:863666. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.863666. eCollection 2022. Front Oncol. 2022. PMID: 35785185 Free PMC article.
-
Osimertinib: A third-generation tyrosine kinase inhibitor for treatment of epidermal growth factor receptor-mutated non-small cell lung cancer with the acquired Thr790Met mutation.J Oncol Pharm Pract. 2018 Jul;24(5):379-388. doi: 10.1177/1078155217712401. Epub 2017 May 31. J Oncol Pharm Pract. 2018. PMID: 28565936 Review.
Cited by
-
Insights into EGFR Mutations and Oncogenic KRAS Mutations in Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer.Cancers (Basel). 2023 Apr 28;15(9):2519. doi: 10.3390/cancers15092519. Cancers (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37173989 Free PMC article.
-
Effectiveness and safety of afatinib, gefitinib, and erlotinib for treatment-naïve elderly patients with epidermal growth factor receptor-mutated advanced non-small-cell lung cancer: a multi-institute retrospective study.Aging (Albany NY). 2024 Jan 8;16(1):550-567. doi: 10.18632/aging.205395. Epub 2024 Jan 8. Aging (Albany NY). 2024. PMID: 38194721 Free PMC article.
-
Favorable Conditions for the Detection of EGFR T790M Mutation Using Plasma Sample in Patients with Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer.Cancers (Basel). 2023 Feb 24;15(5):1445. doi: 10.3390/cancers15051445. Cancers (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36900237 Free PMC article.
-
Strategies and influencing factors for the treatment of advanced non-small cell lung cancer based on epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitors: a narrative review.Transl Cancer Res. 2024 Sep 30;13(9):5123-5140. doi: 10.21037/tcr-24-637. Epub 2024 Sep 5. Transl Cancer Res. 2024. PMID: 39430833 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Response to Brigatinib Targeted Therapy in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Harboring Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor Exon 19 Deletion, T790M, and cis-C797S Triple Mutations: A Case Report.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Dec 29;24(1):602. doi: 10.3390/ijms24010602. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36614045 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Masters G.A., Temin S., Azzoli C.G., Giaccone G., Jr S.B., Brahmer J.R., Ellis P.M., Gajra A., Rackear N., Schiller J.H., et al. Systemic Therapy for Stage IV Non–Small-Cell Lung Cancer: American Society of Clinical Oncology Clinical Practice Guideline Update. J. Clin. Oncol. 2015;33:3488–3515. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2015.62.1342. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Wu Y.L., Planchard D., Lu S., Sun H., Yamamoto N., Kim D.W., Tan D.S.W., Yang J.C., Azrif M., Mitsudomi T., et al. Pan-Asian adapted Clinical Practice Guidelines for the management of patients with metastatic non-small-cell lung cancer: A CSCO-ESMO initiative endorsed by JSMO, KSMO, MOS, SSO and TOS. Ann. Oncol. 2019;30:171–210. doi: 10.1093/annonc/mdy554. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Ahn M.J., Tsai C.M., Shepherd F.A., Bazhenova L., Sequist L.V., Hida T., Yang J.C., Ramalingam S.S., Mitsudomi T., Jänne P.A. Osimertinib in patients with T790M mutation-positive, advanced non–small cell lung cancer: Long-term follow-up from a pooled analysis of 2 phase 2 studies. Cancer. 2019;125:892–901. doi: 10.1002/cncr.31891. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Tan D.S., Yom S.S., Tsao M.S., Pass H.I., Kelly K., Peled N., Yung R.C., Wistuba I.I., Yatabe Y., Unger M., et al. The International Association for the Study of Lung Cancer Consensus Statement on Optimizing Management of EGFR Mutation-Positive Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: Status in 2016. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2016;11:946–963. doi: 10.1016/j.jtho.2016.05.008. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

