Bioinformatics Analysis of the Prognostic Significance of CAND1 in ERα-Positive Breast Cancer
- PMID: 36292029
- PMCID: PMC9600875
- DOI: 10.3390/diagnostics12102327
Bioinformatics Analysis of the Prognostic Significance of CAND1 in ERα-Positive Breast Cancer
Abstract
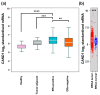
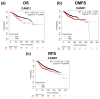
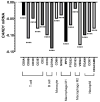
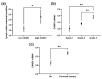
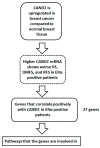
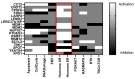
The identification of novel prognostic biomarkers for breast cancer is an unmet clinical need. Cullin-associated and neddylation-dissociated 1 (CAND1) has been implicated in mediating carcinogenesis in prostate and lung cancers. In addition, CAND1 is an established prognostic biomarker for worse prognosis in liver cancer. However, the prognostic significance of CAND1 in breast cancer has not yet been explored. In this study, Breast Cancer Gene-Expression Miner (Bc-GenExMiner) and TIMER2.0 were utilized to explore the mRNA expression of CAND1 in ERα-positive breast cancer patients. The Kaplan-Meier plotter was used to explore the relationship between CAND1 expression and several prognostic indicators. The Gene Set Cancer Analysis (GSCA) web server was then used to explore the pathways of the genes that correlate with CAND1 in ERα-positive breast cancer. Immune infiltration was investigated using Bc-GenExMiner. Our bioinformatics analysis illustrates that breast cancer patients have higher CAND1 compared to normal breast tissue and that ERα-positive breast cancer patients with a high expression of CAND1 have poor overall survival (OS), distant metastasis-free survival (DMFS), and relapse-free survival (RFS) outcomes. Higher CAND1 expression was observed in histologic grade 3 compared to grades 2 and 1. Our results revealed that CAND1 positively correlates with lymph nodes and negatively correlates with the infiltration of immune cells, which is in agreement with published reports. Our findings suggest that CAND1 might mediate invasion and metastasis in ERα-positive breast cancer, possibly through the activation of estrogen and androgen signaling pathways; however, experiments should be carried out to further explore the role of CAND1 in activating the androgen and estrogen signaling pathways. In conclusion, the results suggest that CAND1 could be used as a potential novel biomarker for worse prognosis in ERα-positive breast cancer.
Keywords: CAND1; Erα; bioinformatics; breast cancer; metastasis; prognosis; survival.
Conflict of interest statement
The author declares no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Bioinformatics Identification of TUBB as Potential Prognostic Biomarker for Worse Prognosis in ERα-Positive and Better Prognosis in ERα-Negative Breast Cancer.Diagnostics (Basel). 2022 Aug 26;12(9):2067. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics12092067. Diagnostics (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36140469 Free PMC article.
-
Increased Expression of INHBA Is Correlated With Poor Prognosis and High Immune Infiltrating Level in Breast Cancer.Front Bioinform. 2022 Mar 24;2:729902. doi: 10.3389/fbinf.2022.729902. eCollection 2022. Front Bioinform. 2022. PMID: 36304286 Free PMC article.
-
RUNX1T1, a potential prognostic marker in breast cancer, is co-ordinately expressed with ERα, and regulated by estrogen receptor signalling in breast cancer cells.Mol Biol Rep. 2021 Jul;48(7):5399-5409. doi: 10.1007/s11033-021-06542-3. Epub 2021 Jul 15. Mol Biol Rep. 2021. PMID: 34264479
-
Bioinformatics analysis of prognostic significance of COL10A1 in breast cancer.Biosci Rep. 2020 Feb 28;40(2):BSR20193286. doi: 10.1042/BSR20193286. Biosci Rep. 2020. PMID: 32043519 Free PMC article.
-
Bioinformatics analysis revealing prognostic significance of RRM2 gene in breast cancer.Biosci Rep. 2019 Apr 9;39(4):BSR20182062. doi: 10.1042/BSR20182062. Print 2019 Apr 30. Biosci Rep. 2019. PMID: 30898978 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Dysregulation of the DRAIC/SBK1 Axis Promotes Lung Cancer Progression.Diagnostics (Basel). 2024 Oct 5;14(19):2227. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics14192227. Diagnostics (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39410631 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Helmstaedt K., Schwier E., Christmann M., Nahlik K., Westermann M., Harting R., Grond S., Busch S., Braus G. Recruitment of the inhibitor Cand1 to the cullin substrate adaptor site mediates interaction to the neddylation site. Mol. Biol. Cell. 2011;22:153–164. doi: 10.1091/mbc.e10-08-0732. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

