Detection and Classification of Knee Osteoarthritis
- PMID: 36292051
- PMCID: PMC9600223
- DOI: 10.3390/diagnostics12102362
Detection and Classification of Knee Osteoarthritis
Abstract
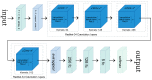
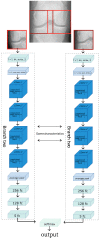
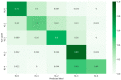
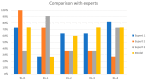
Osteoarthritis (OA) affects nearly 240 million people worldwide. Knee OA is the most common type of arthritis, especially in older adults. Physicians measure the severity of knee OA according to the Kellgren and Lawrence (KL) scale through visual inspection of X-ray or MR images. We propose a semi-automatic CADx model based on Deep Siamese convolutional neural networks and a fine-tuned ResNet-34 to simultaneously detect OA lesions in the two knees according to the KL scale. The training was done using a public dataset, whereas the validations were performed with a private dataset. Some problems of the imbalanced dataset were solved using transfer learning. The model results average of the multi-class accuracy is 61%, presenting better performance results for classifying classes KL-0, KL-3, and KL-4 than KL-1 and KL-2. The classification results were compared and validated using the classification of experienced radiologists.
Keywords: CAD; CNN; KL grades; OA knee; X-ray images; deep learning; osteoarthritis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Kalo K., Niederer D., Schmitt M., Vogt L. Acute effects of a single bout of exercise therapy on knee acoustic emissions in patients with osteoarthritis: A double-blinded, randomized controlled crossover trial. BMC Musculoskelet. Disord. 2022;23:657. doi: 10.1186/s12891-022-05616-y. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

