Machine Learning Models for the Prediction of Renal Failure in Chronic Kidney Disease: A Retrospective Cohort Study
- PMID: 36292142
- PMCID: PMC9600783
- DOI: 10.3390/diagnostics12102454
Machine Learning Models for the Prediction of Renal Failure in Chronic Kidney Disease: A Retrospective Cohort Study
Abstract
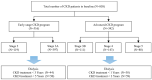
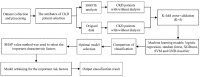
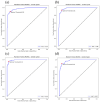
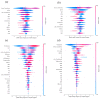
This study assessed the feasibility of five separate machine learning (ML) classifiers for predicting disease progression in patients with pre-dialysis chronic kidney disease (CKD). The study enrolled 858 patients with CKD treated at a veteran's hospital in Taiwan. After classification into early and advanced stages, patient demographics and laboratory data were processed and used to predict progression to renal failure and important features for optimal prediction were identified. The random forest (RF) classifier with synthetic minority over-sampling technique (SMOTE) had the best predictive performances among patients with early-stage CKD who progressed within 3 and 5 years and among patients with advanced-stage CKD who progressed within 1 and 3 years. Important features identified for predicting progression from early- and advanced-stage CKD were urine creatinine and serum creatinine levels, respectively. The RF classifier demonstrated the optimal performance, with an area under the receiver operating characteristic curve values of 0.96 for predicting progression within 5 years in patients with early-stage CKD and 0.97 for predicting progression within 1 year in patients with advanced-stage CKD. The proposed method resulted in the optimal prediction of CKD progression, especially within 1 year of advanced-stage CKD. These results will be useful for predicting prognosis among patients with CKD.
Keywords: kidney disease; random forest; renal dialysis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Predicting the Progression of Chronic Kidney Disease: A Systematic Review of Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning Approaches.Cureus. 2024 May 12;16(5):e60145. doi: 10.7759/cureus.60145. eCollection 2024 May. Cureus. 2024. PMID: 38864072 Free PMC article. Review.
-
CKD Progression Prediction in a Diverse US Population: A Machine-Learning Model.Kidney Med. 2023 Jun 24;5(9):100692. doi: 10.1016/j.xkme.2023.100692. eCollection 2023 Sep. Kidney Med. 2023. PMID: 37637863 Free PMC article.
-
An efficient ensemble based machine learning approach for predicting Chronic Kidney Disease.Curr Med Imaging. 2023 May 8. doi: 10.2174/1573405620666230508104538. Online ahead of print. Curr Med Imaging. 2023. PMID: 37157217
-
Short Timeframe Prediction of Kidney Failure among Patients with Advanced Chronic Kidney Disease.Clin Chem. 2023 Oct 3;69(10):1163-1173. doi: 10.1093/clinchem/hvad112. Clin Chem. 2023. PMID: 37522430
-
Using Data Mining Techniques to Predict Chronic Kidney Disease: A Review Study.Int J Prev Med. 2023 Aug 28;14:110. doi: 10.4103/ijpvm.ijpvm_482_21. eCollection 2023. Int J Prev Med. 2023. PMID: 37855011 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Predicting the Progression of Chronic Kidney Disease: A Systematic Review of Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning Approaches.Cureus. 2024 May 12;16(5):e60145. doi: 10.7759/cureus.60145. eCollection 2024 May. Cureus. 2024. PMID: 38864072 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Klotho-Based Machine Learning Model for Prediction of both Kidney and Cardiovascular Outcomes in Chronic Kidney Disease.Kidney Dis (Basel). 2024 Mar 25;10(3):200-212. doi: 10.1159/000538510. eCollection 2024 Jun. Kidney Dis (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38835404 Free PMC article.
-
Development and validation of a machine learning model to predict time to renal replacement therapy in patients with chronic kidney disease.BMC Nephrol. 2024 Mar 16;25(1):101. doi: 10.1186/s12882-024-03527-9. BMC Nephrol. 2024. PMID: 38493099 Free PMC article.
-
Predicting CKD progression using time-series clustering and light gradient boosting machines.Sci Rep. 2024 Jan 19;14(1):1723. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-52251-9. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 38242985 Free PMC article.
-
Artificial intelligence in predicting chronic kidney disease prognosis. A systematic review and meta-analysis.Ren Fail. 2024 Dec;46(2):2435483. doi: 10.1080/0886022X.2024.2435483. Epub 2024 Dec 11. Ren Fail. 2024. PMID: 39663146 Free PMC article.
References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

