Utility of Endoscopic Ultrasound-Guided Fine-Needle Aspiration and Biopsy for Histological Diagnosis of Type 2 Autoimmune Pancreatitis
- PMID: 36292153
- PMCID: PMC9601245
- DOI: 10.3390/diagnostics12102464
Utility of Endoscopic Ultrasound-Guided Fine-Needle Aspiration and Biopsy for Histological Diagnosis of Type 2 Autoimmune Pancreatitis
Abstract
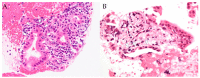
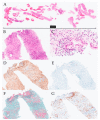
In Japan, type 1 autoimmune pancreatitis (AIP) is the most common type of AIP; type 2 AIP is rare. The aim of this study was to clarify the usefulness of endoscopic ultrasound-guided fine-needle aspiration and biopsy (EUS-FNAB) for the diagnosis of type 2 AIP. We analyzed the tissue specimens of 10 patients with suspected type 2 AIP who underwent EUS-FNAB at our hospital between April 2009 and March 2021 for tissue volume and histopathological diagnostic performance. The male-to-female ratio of the patients was 8:2, and the patient age (mean ± standard deviation) was 35.6 ± 15.5 years. EUS-FNAB provided sufficient tissue volume, with high-power field >10 in eight patients (80.0%). Based on the International Consensus Diagnostic Criteria (ICDC), four patients (40.0%) had histological findings corresponding to ICDC level 1, and five patients (50.0%) had histological findings corresponding to ICDC level 2. The results of this study show that EUS-FNB can be considered an alternative method to resection and core-needle biopsy for the collection of tissue samples of type 2 AIP.
Keywords: International Consensus Diagnostic Criteria; granulocytic epithelial lesions; inflammatory bowel disease; main pancreatic duct narrowing; ulcerative colitis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Shimosegawa T., Chari S.T., Frulloni L., Kamisawa T., Kawa S., Mino-Kenudson M., Kim M.H., Klöppel G., Lerch M.M., Löhr M., et al. International consensus diagnostic criteria for autoimmune pancreatitis: Guidelines of the International Association of Pancreatology. Pancreas. 2011;40:352–358. doi: 10.1097/MPA.0b013e3182142fd2. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Löhr J.M., Beuers U., Vujasinovic M., Alvaro D., Frøkjær J.B., Buttgereit F., Capurso G., Culver E.L., de-Madaria E., Della-Torre E., et al. European guideline on IgG4-related digestive disease—UEG and SGF evidence-based recommendations. United Eur. Gastroenterol. J. 2020;8:637–666. doi: 10.1177/2050640620934911. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Stone J.H., Khosroshahi A., Deshpande V., Chan J.K., Heathcote J.G., Aalberse R., Azumi A., Bloch D.B., Brugge W.R., Carruthers M.N., et al. Recommendations for the nomenclature of IgG4-related disease and its individual organ system manifestations. Arthritis Rheum. 2012;64:3061–3067. doi: 10.1002/art.34593. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Kamisawa T., Kim M.H., Liao W.C., Liu Q., Balakrishnan V., Okazaki K., Shimosegawa T., Chung J.B., Lee K.T., Wang H.P., et al. Clinical characteristics of 327 Asian patients with autoimmune pancreatitis based on Asian diagnostic criteria. Pancreas. 2011;40:200–205. doi: 10.1097/MPA.0b013e3181fab696. - DOI - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

