Automatic Cardiopulmonary Endurance Assessment: A Machine Learning Approach Based on GA-XGBOOST
- PMID: 36292227
- PMCID: PMC9600669
- DOI: 10.3390/diagnostics12102538
Automatic Cardiopulmonary Endurance Assessment: A Machine Learning Approach Based on GA-XGBOOST
Abstract
Objective: Among various assessment paradigms, the cardiopulmonary exercise test (CPET) provides rich evidence as part of the cardiopulmonary endurance (CPE) assessment. However, methods and strategies for interpreting CPET results are not in agreement. The purpose of this study is to validate the possibility of using machine learning to evaluate CPET data for automatically classifying the CPE level of workers in high-latitude areas.
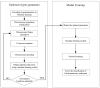
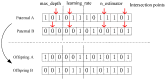
Methods: A total of 120 eligible workers were selected for this cardiopulmonary exercise experiment, and the physiological data and completion of the experiment were recorded in the simulated high-latitude workplace, within which 84 sets of data were used for XGBOOST model training and36 were used for the model validation. The model performance was compared with Support Vector Machine and Random Forest. Furthermore, hyperparameter optimization was applied to the XGBOOST model by using a genetic algorithm.
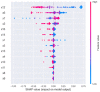
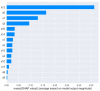
Results: The model was verified by the method of tenfold cross validation; the correct rate was 0.861, with a Micro-F1 Score of 0.864. Compared with RF and SVM, all data achieved a better performance.
Conclusion: With a relatively small number of training samples, the GA-XGBOOST model fits well with the training set data, which can effectively evaluate the CPE level of subjects, and is expected to provide automatic CPE evaluation for selecting, training, and protecting the working population in plateau areas.
Keywords: CPET; XG-BOOST; cardiopulmonary assessment.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures







Similar articles
-
Machine learning models for reinjury risk prediction using cardiopulmonary exercise testing (CPET) data: optimizing athlete recovery.BioData Min. 2025 Feb 17;18(1):16. doi: 10.1186/s13040-025-00431-2. BioData Min. 2025. PMID: 39962522 Free PMC article.
-
Neural network methods for diagnosing patient conditions from cardiopulmonary exercise testing data.BioData Min. 2022 Aug 13;15(1):16. doi: 10.1186/s13040-022-00299-6. BioData Min. 2022. PMID: 35964102 Free PMC article.
-
An optimized XGBoost-based machine learning method for predicting wave run-up on a sloping beach.MethodsX. 2023 Mar 10;10:102119. doi: 10.1016/j.mex.2023.102119. eCollection 2023. MethodsX. 2023. PMID: 37007622 Free PMC article.
-
Do we need different machine learning algorithms for QSAR modeling? A comprehensive assessment of 16 machine learning algorithms on 14 QSAR data sets.Brief Bioinform. 2021 Jul 20;22(4):bbaa321. doi: 10.1093/bib/bbaa321. Brief Bioinform. 2021. PMID: 33313673
-
CS-GA-XGBoost-Based Model for a Radio-Frequency Power Amplifier under Different Temperatures.Micromachines (Basel). 2023 Aug 27;14(9):1673. doi: 10.3390/mi14091673. Micromachines (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37763836 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Hyperparameter Optimization with Genetic Algorithms and XGBoost: A Step Forward in Smart Grid Fraud Detection.Sensors (Basel). 2024 Feb 15;24(4):1230. doi: 10.3390/s24041230. Sensors (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38400385 Free PMC article.
-
The interpretable machine learning model for depression associated with heavy metals via EMR mining method.Sci Rep. 2025 Mar 28;15(1):10811. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-95938-3. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40155474 Free PMC article.
-
Feasibility study of rehabilitation for cardiac patients aided by an artificial intelligence web-based programme: a randomised controlled trial (RECAP trial)-a study protocol.BMJ Open. 2024 Apr 30;14(4):e079404. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2023-079404. BMJ Open. 2024. PMID: 38688664 Free PMC article.
-
The interpretable machine learning model associated with metal mixtures to identify hypertension via EMR mining method.J Clin Hypertens (Greenwich). 2024 Feb;26(2):187-196. doi: 10.1111/jch.14768. Epub 2024 Jan 12. J Clin Hypertens (Greenwich). 2024. PMID: 38214193 Free PMC article.
-
Assessment of EMR ML Mining Methods for Measuring Association between Metal Mixture and Mortality for Hypertension.High Blood Press Cardiovasc Prev. 2024 Sep;31(5):473-483. doi: 10.1007/s40292-024-00666-w. Epub 2024 Aug 12. High Blood Press Cardiovasc Prev. 2024. PMID: 39133252 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Amelchugov S., Inzhutov I., Nikitina O., Berseneva M. On the issue of personnel management in high-latitude construction. MATEC Web Conf. 2018;245:03021. doi: 10.1051/matecconf/201824503021. - DOI
-
- Huang B. Ph.D thesis. Tianjin Institute of Physical Education; Tianjin, China: 2020. Analysis and Comprehensive Evaluation of Core Elements of Physical Fitness of Young Male at Different Altitudes.
-
- Balady G.J., Arena R., Sietsema K., Myers J., Coke L., Fletcher G.F., Forman D., Franklin B., Guazzi M., Gulati M., et al. Clinician’s guide to cardiopulmonary exercise testing in adults: A scientific statement from the American Heart Association. Circulation. 2010;122:191–225. doi: 10.1161/CIR.0b013e3181e52e69. - DOI - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

