Recent Advancements in Emerging Technologies for Healthcare Management Systems: A Survey
- PMID: 36292387
- PMCID: PMC9601636
- DOI: 10.3390/healthcare10101940
Recent Advancements in Emerging Technologies for Healthcare Management Systems: A Survey
Abstract
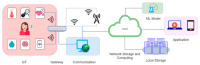
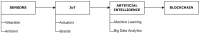
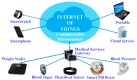
In recent times, the growth of the Internet of Things (IoT), artificial intelligence (AI), and Blockchain technologies have quickly gained pace as a new study niche in numerous collegiate and industrial sectors, notably in the healthcare sector. Recent advancements in healthcare delivery have given many patients access to advanced personalized healthcare, which has improved their well-being. The subsequent phase in healthcare is to seamlessly consolidate these emerging technologies such as IoT-assisted wearable sensor devices, AI, and Blockchain collectively. Surprisingly, owing to the rapid use of smart wearable sensors, IoT and AI-enabled technology are shifting healthcare from a conventional hub-based system to a more personalized healthcare management system (HMS). However, implementing smart sensors, advanced IoT, AI, and Blockchain technologies synchronously in HMS remains a significant challenge. Prominent and reoccurring issues such as scarcity of cost-effective and accurate smart medical sensors, unstandardized IoT system architectures, heterogeneity of connected wearable devices, the multidimensionality of data generated, and high demand for interoperability are vivid problems affecting the advancement of HMS. Hence, this survey paper presents a detailed evaluation of the application of these emerging technologies (Smart Sensor, IoT, AI, Blockchain) in HMS to better understand the progress thus far. Specifically, current studies and findings on the deployment of these emerging technologies in healthcare are investigated, as well as key enabling factors, noteworthy use cases, and successful deployments. This survey also examined essential issues that are frequently encountered by IoT-assisted wearable sensor systems, AI, and Blockchain, as well as the critical concerns that must be addressed to enhance the application of these emerging technologies in the HMS.
Keywords: artificial intelligence; blockchain; healthcare; internet of things; sensors; wearables.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures





References
-
- Fan Y., Xu P., Jin H., Ma J., Qin L. Vital sign measurement in telemedicine rehabilitation based on intelligent wearable medical devices. Ieee Access. 2019;7:54819–54823. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2913189. - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

